Gaza Strip
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Middle Eastern Countries
| قطاع غزة Gaza Strip
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Largest city | Gaza City | |
| Official languages | Arabic ( de facto) | |
| Government | Hamas-led government | |
| - | Prime Minister | Ismail Haniyeh ( Hamas) |
| - | President of the Palestinian National Authority | Mahmoud Abbas ( Fatah) |
| Organized | September 13, 1993 Oslo accords | |
| - | Signed | PA took partial control in May 1994, and full control in September 2005 (Israel retains control of airspace and offshore maritime access) |
| Area | ||
| - | Total | 360 km² ( 212th) 130 sq mi |
| Population | ||
| - | 2007 estimate | 1,482,405 ( 151st1) |
| - | Density | 3,823/km² ( 6th1) 10,586/sq mi |
| GDP ( PPP) | estimate | |
| - | Total | $770 million ( 160th1) |
| - | Per capita | 600 $ ( 167th1) |
| Currency | Israeli new sheqel (de facto) ( ILS) |
|
| Time zone | ( UTC+2) | |
| - | Summer ( DST) | ( UTC+3) |
| Calling code | +970 | |
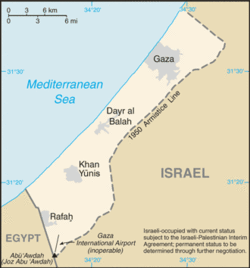
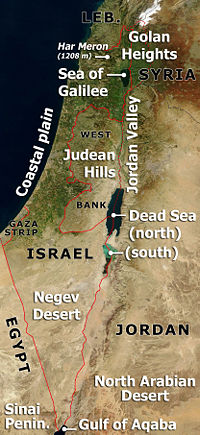
The Gaza Strip (Arabic: قطاع غزة transliteration: Qitˁɑ' Ġazzah/Qita' Ghazzah, Hebrew: רצועת עזה Retzu'at 'Azza) is a coastal strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea, bordering Egypt on the south-west and Israel on the north and east. It is about 41 kilometers (25 mi) long, and between 6 and 12 kilometers (4–7.5 mi) wide, with a total area of 360 square kilometers (139 sq mi).
Israel oversees the strip's airspace, territorial water and offshore maritime access. Israel's control of access to Gaza has been controversial. Israel also controls the population registry, entry of foreigners, imports and exports as well as the tax system.
The territory takes its name from Gaza, its main city. It has about 1.4 million Palestinian (or Gazan) residents.
The Strip itself and its population are nominally governed by the Palestinian National Authority, though following the June 2007 battle of Gaza, actual control is in the hands of the de facto government dominated by Hamas. The Gaza Strip is not recognized internationally as part of any sovereign country.
History
Ancient history until mid 16th century (15th century BC-1517)
The first recorded mention of the city of Gaza was a reference by Pharaoh Thutmose II (18th dynasty; 15th century BC), though the actual habitation no doubt predates that official record. It is also mentioned in the Tell el-Amarna tablets, the diplomatic and administrative records of ancient Egypt.
Because of its strategic position on the Via Maris (see map), the ancient coastal road linking Egypt with Palestine and the lands beyond, Gaza experienced little peace in antiquity. Throughout its history it was a prosperous trade centre, sitting as it does on the ancient Sea Road.
The area was under Egyptian occupation for over 300 years when the Philistines took control and settled the city and surrounding area. Gaza became an important Philistine trading centre and part of the Pentapolis (league of five cities).
The Bible makes a reference to Gaza as the place where Samson was delivered into bondage by Delilah and where he died while toppling the temple of the god Dagon. It fell to the Israelite King David in 1000 BC.
The area fell to the Assyrians in 732 BC, to the Egyptians, to the Babylonians in 586 BC, Persians in 525 BC, and the Macedonians. Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great met stiff resistance there in 332 BC. After conquering it, he sold its inhabitants into slavery.
In 145 BC Gaza was conquered by Jonathan the Hasmonean (Brother of Judah the Maccabee). In Hellenistic and Roman times the harbour, about 3 miles (5 km) from the city proper, was called Neapolis (Greek: “New City”).
It was conquered by Arabs in the 630s after a siege during which the Jewish population of the city defended it alongside the Byzantine garrison. Believed to be the site where Muhammad's great grandfather was buried, the city became an important Islamic centre. In the 12th century, Gaza was taken by Christian Crusaders; it returned to Muslim control in 1187.
Ottoman and British control (1517-1948)
In 1517 Gaza fell to the Ottomans and was part of the Ottoman Empire until the First World War.
Starting in the early 19th century, Gaza was culturally dominated by neighboring Egypt. Though part of the Ottoman Empire, a large number of its residents were Egyptians (and their descendants) who had fled political turmoil.
The region served as a battlefield during the First World War (1914-18). The Gaza Strip was taken by the British in the Third Battle of Gaza on 7 November 1917.
Following World War I, Gaza became part of the British mandate for Palestine under the authority of the League of Nations.
British rule of Palestine ended with the Israeli War of Independence in 1948.
Egyptian Control (1948-67)
According to the terms of the 1947 United Nations partition plan, the Gaza area was to become part of a new Palestinian Arab state. Following the dissolution of the British mandate of Palestine and 1947-1948 Civil War in Palestine, Israel declared its independence in May 1948. The Egyptian army invaded the area from the south, starting the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
The Gaza Strip as it is known today was the product of the subsequent 1949 Armistice Agreements between Egypt and Israel, often referred to as the Green Line. Egypt occupied the Strip from 1949 (except for four months of Israeli occupation during the 1956 Suez Crisis) until 1967. The Strip's population was greatly augmented by an influx of Palestinian Arab refugees who fled or were expelled from Israel during the fighting.
Towards the end of the war, the All-Palestine Government (Arabic: حكومة عموم فلسطين hukumat 'umum Filastin) was proclaimed in Gaza City on 22 September 1948 by the Arab League. It was conceived partly as an Arab League attempt to limit the influence of Transjordan over the Palestinian issue. The government was not recognized by Transjordan or any non-Arab country. It was little more than a façade under Egyptian control, had negligible influence or funding, and subsequently moved to Cairo. Palestinians living in the Gaza Strip or Egypt were issued All-Palestine passports until 1959, when Gamal Abdul Nasser, President of Egypt, annulled the All-Palestine government by decree.
Egypt never annexed the Gaza Strip, but instead treated it as a controlled territory and administered it through a military governor. The refugees were never offered Egyptian citizenship . During the Sinai campaign of November 1956, the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula were overrun by Israeli troops. International pressure soon forced Israel to withdraw.
Israel occupied the Gaza Strip during the 1967 Six Day War.
Israeli occupation (1967-2005)
The area was again occupied, this time by Israel from the Six-Day War in June 1967. The military occupation lasted for 38 years, until 2005. However, Israel retains control of air space, territorial waters, offshore maritime access, the population registry, entry of foreigners, imports and exports as well as the tax system.
During the period of Israeli occupation, Israel created a settlement bloc, Gush Katif in the south west corner of the Strip near Rafah near the Egyptian border. Besides ideological reasons for being there, the settlement bloc also served Israel's security concerns. The Gaza Strip remained under Israeli military administration until 1994. During that period the military administration was also responsible for the maintenance of civil facilities and services.
In March 1979 Israel and Egypt signed the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty. Among other things, the treaty provided for the withdrawal by Israel of its armed forces and civilians from the Sinai Peninsula which Israel had captured during the 1967 Six-Day War. The final status of the Gaza Strip as with relations between Israel and Palestinians was not dealt with in the treaty. The treaty did settle the international border between Gaza Strip and Egypt. Egypt renounced all territorial claims to the region beyond the international border.
In May 1994, following the Palestinian-Israeli agreements known as the Oslo Accords, a phased transfer of governmental authority to the Palestinians took place. Much of the Strip (except for the settlement blocs and military areas) came under Palestinian Authority control. The Israeli forces left Gaza City and other urban areas, leaving the new Palestinian Authority to administer and police the Strip. The Palestinian Authority, led by Yasser Arafat, chose Gaza City as its first provincial headquarters. In September 1995, Israel and the PLO signed a second peace agreement extending the Palestinian Authority to most West Bank towns. The agreement also established an elected 88-member Palestinian National Council, which held its inaugural session in Gaza in March 1996.
The Second Intifada broke out in September 2000. In February 2005, the Israeli government voted to implement a unilateral disengagement plan from the Gaza Strip. The plan began to be implemented on 15 August 2005 (the day after Tisha B'av) and was completed on 12 September 2005. Under the plan, all Israeli settlements in the Gaza Strip (and four in the West Bank) and the nearby Erez bloc were dismantled with the removal of all 9,000 Israeli settlers (most of them in the Gush Katif settlement area in the Strip's southwest) and military bases. On 12 September 2005 the Israeli cabinet formally declared an end to military rule in the Gaza Strip after 38 years of control. To avoid any allegation that it was still in occupation of any part of the Gaza Strip, Israel also withdrew from the Philadelphi Route, which is a narrow strip adjacent to the Strip's border with Egypt, after Egypt's agreement to secure its side of the border. Under the Oslo Accords the Philadelphi Route was to remain under Israeli control, to prevent the smuggling of materials (such as ammunition) and people across the border with Egypt. With Egypt agreeing to patrol its side of the border, it was hoped that the objective would be achieved.
Palestinian Authority control (2005-2007)
In accordance with the Oslo Accords, the Palestinian Authority took over the administrative authority of the Gaza Strip (other than the settlement blocs and military areas) in 1994. After the complete Israeli withdrawal of Israeli settlers and military from the Gaza Strip on 12 September 2005, the Palestinian Authority had complete administrative authority in the Gaza Strip.
Palestinians maintain that the Israeli occupation is not over because Israel still controls Gazan borders, airspace and territorial waters. The Israeli human rights organization B'tselem said in November 2006 that "the broad scope of Israeli control in the Gaza Strip creates a strong case for the claim that Israel's occupation of the Gaza Strip continue." University of London, School of Oriental and African Studies, law professor Iain Scobbie noted in 2006 that "Israel retains absolute authority over Gaza’s airspace and territorial sea. It is manifestly exercising governmental authority in these areas.... it is clear that Israeli withdrawal of land forces did not terminate occupation." And according to some Palestinians, Israel's occupation of the Gaza Strip continued. "They control the water, the sky and the passages. How can you say occupation is over?" said Palestinian negotiator Saeb Erekat in 2005. Similar viewpoints have been presented by many other Palestinian organizations and leaders. The Al Mezan Centre for Human Rights also argues that the Gaza Strip remains occupied by Israel.
Prior to Israel's withdrawal from the Gaza Strip, the United States considered the Gaza Strip to be an Israel-occupied territory. Following the withdrawal, no official US government statement has been made on the status of the Strip. However, the CIA World Factbook (which is an official U.S. government publication), which was last updated in 2007, continues to list the Gaza Strip as an Israeli-occupied territory.
Hamas won the 2006 Palestinian legislative elections. However, when a Hamas-controlled government was formed, continuing to refuse to recognise Israel, renounce violence and agree to honour agreements previously made by the PLO, Israel, the United States, Canada, and the European Union froze all funds to the Hamas-controlled government. They view Hamas as a terrorist organization.
In December 2006, news reports indicated that a number of Palestinians were leaving the Gaza Strip, due to political disorder and economic stagnation there.
In January 2007, fighting continued between Hamas and Fatah, without any progress towards resolution or reconciliation. The worst clashes occurred in the northern Gaza Strip, where Gen. Muhammed Gharib, a senior commander of the Fatah-dominated Preventative Security Force, was killed when a rocket hit his home. Gharib's two daughters and two bodyguards were also killed in the attack, which was carried out by Hamas gunmen.
At the end of January 2007, it appeared that a newly-negotiated truce between Fatah and Hamas was starting to take hold . However, after a few days, new fighting broke out. Fatah fighters stormed a Hamas-affiliated university in the Gaza Strip. Officers from Abbas' presidential guard battled Hamas gunmen guarding the Hamas-led Interior Ministry.
In May 2007, the deal between Hamas and Fatah appeared to be weaker, as new fighting broke out between the factions. This was considered a major setback. Interior Minister Hani Qawasmi, who had been considered a moderate civil servant acceptable to both factions, resigned due to what he termed harmful behaviour by both factions.
Fighting spread in the Gaza Strip with both factions attacking vehicles and facilities of the other side. In response to constant attacks by rocket fire from the Gaza Strip, Israel launched an air strike which destroyed a building used by Hamas. Some Palestinians said the violence could bring the end of the Fatah-Hamas coalition government, and possibly the end of the Palestinian authority.
Hamas spokeman Moussa Abu Marzouk placed the blame for the worsening situation in the Strip upon Israel, stating that the constant pressure of economic sanctions upon Gaza resulted in the "real explosion". Expressions of concerns were received from many Arab leaders, with many offering to try to help by doing some diplomatic work between the two factions. One journalist wrote an eyewitness account stating:
Today I have seen people shot before my eyes, I heard the screams of terrified women and children in a burning building, and I argued with gunmen who wanted to take over my home. I have seen a lot in my years as a journalist in Gaza, but this is the worst it's been.
Hamas (2007-Present)
In June 2007, the Palestinian Civil War between Hamas (Islamic Resistance Movement) and Fatah (Palestine Liberation Movement) intensified. Hamas routed Fatah, and by 14 June 2007, the Gaza Strip was completely overrun by Hamas, resulting in a de facto government maintaining it is the legitimate government of the Palestinian Authority. Retaliation by Fatah against Hamas in the West Bank has led to the opposite result there.
Hamas continues to consolidate its position in Gaza. It has ousted Fatah-linked officials from positions of power and authority in the Strip (such as government positions, security services, universities, newspapers etc) and is in the process of consolidating its monopoly of fire power by progressively removing guns from the hands of peripheral militias, clans, and criminal groups. It is also harassing journalists.
While clamping down on lawlessness in the Strip, it has made no effort to control the continued firing of Qassam rockets from the Strip across the border into Israel, targeted at Israeli civilians. In response, Israel has regularly threatened to close every access to the Gaza strip, until the 19th of January 2008, when Israel stopped all humanitarian support, causing power outages.
Current status
The Palestinian Authority has been responsible for the civil and security administration in the Gaza Strip since 1994. There have been no Israeli settlements or military bases in the Gaza strip since the unilateral disengagement on 12 September 2005.
After Hamas' takeover in Gaza on 14 June 2007, Palestinian Authority Chairman Mahmoud Abbas of Fatah dismissed Hamas from the government and formed a Cabinet based in the West Bank. Abbas' government has won widespread international support. Egypt, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia said in late June 2007 that the West Bank-based Cabinet formed by Abbas was the sole legitimate Palestinian government, and Egypt moved its embassy from Gaza to the West Bank. . Hamas, which has effective control of the Strip, faces international diplomatic and economic isolation.
Nevertheless, the Gaza Strip has been under the effective control of Hamas since June 14, 2007. Hamas also effectively controls the Strip's international border with Egypt, as well as with Israel (subject to equal corresponding control by the other side). However under the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty of 1979 the only crossing between Gaza and Egypt is to be through the Rafah Border Crossing. Since the unilateral disengagement in September 2005 this crossing has been supervised by EU Border Assistance Mission Rafah under a separate Agreement finalised in November 2005. Since the Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip, the monitors have not been able to perform their functions under the Agreement, citing security concerns, resulting in the Rafah Crossing being closed. The only land access into the Strip to Israel is via the Erez and Karni crossings.
On January 23, 2008, Palestinian militants destroyed several parts of the wall dividing Gaza and Egypt in the town of Rafah. Thousands of Gazans crossed the border seeking food and supplies. Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak ordered his troops to allow the Palestinians in, due to the crisis, but to verify that they did not bring weapons back. At the same time, Israel increased its state of alert along the length of the Israel-Egypt Sinai border, and warned its citizens to leave Sinai "without delay". The EU Border Monitors have indicated their readiness to return to monitor the border, should Hamas guarantee their safety; while the Palestinian Authority has demanded that Egypt deal only with the Authority in negotiations relating to borders. Israel has eased up some influx of goods and medical supplies to the strip while Hamas and Egypt have shored up some of the gaping holes between the two areas and with the weather, cold,windy, and rainy the flow of people has shrunk to a trickle.
Geography
|
|||
The Gaza Strip is located in the Middle East (at ). It has a 51 kilometers (32 mi) border with Israel, and an 11 km border with Egypt, near the city of Rafah. Khan Yunis is located 7 kilometers (4 mi) northeast of Rafah, and several towns around Deir el-Balah are located along the coast between it and Gaza City. Beit Lahia and Beit Hanoun are located to the north and northeast of Gaza City, respectively. The Gush Katif bloc of Israeli localities used to exist on the sand dunes adjacent to Rafah and Khan Yunis, along the southwestern edge of the 40 kilometers (25 mi) Mediterranean coastline.
Gaza strip has a temperate climate, with mild winters, and dry, hot summers subject to drought. The terrain is flat or rolling, with dunes near the coast. The highest point is Abu 'Awdah (Joz Abu 'Auda), at 105 meters (344 ft) above sea level. Natural resources include arable land (about a third of the strip is irrigated), and recently discovered natural gas. Environmental issues include desertification; salination of fresh water; sewage treatment; water-borne disease; soil degradation; and depletion and contamination of underground water resources.
The Strip currently holds the oldest known remains of a man-made bonfire, and some of the world's oldest dated human skeletons. It occupies territory similar to that of ancient Philistia, and is occasionally known by that name.
Demographics
In 2007 approximately 1.48 million Palestinians live in the Gaza Strip, of whom almost 1.0 million are UN-registered refugees. The majority of the Palestinians are descendants of refugees who fled or were expelled from their homes during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. The Strip's population has continued to increase since that time, one of the main reasons being a total fertility rate of more than 5 children per woman. In a ranking by total fertility rate, this places Gaza 19th of 222 regions.
The vast majority of the population are Sunni Muslims, with an estimated 2,000 to 3,000 Christians. The Christian population has been shrinking since Hamas' takeover, due to tensions with the Muslim community and economic sanctions imposed by Israel. In December 2007, Israel has permitted 400 Gaza Christians to travel through Israel to Bethlehem for Christmas. While they are strictly travel permits, many Christian families are taking the opportunity to settle in the West Bank, despite the illegality.
Of the largest foreign communities in the Gaza Strip was the approximately 500 women from the former Soviet Union. During the Soviet era, the Communist Party subsidized university studies for thousands of students from Yemen, Egypt, Syria and the territories. Some of them got married during their studies and brought their Russian and Ukrainian wives back home. However, over half of them were able to leave the Strip via the Erez crossing to Amman within days of Hamas' takeover. From there they have flown back to Eastern Europe.
Economy
Economic output in the Gaza Strip declined by about one-third between 1992 and 1996. This downturn has been variously attributed to corruption and mismanagement by Yasser Arafat, and to Israeli closure policies—the imposition of generalized border closures which disrupted previously established labor and commodity market relationships between Israel and the Strip. A serious negative social effect of this downturn was the emergence of high unemployment.
Israel's use of comprehensive closures decreased during the next few years and, in 1998, Israel implemented new policies to reduce the impact of closures and other security procedures on the movement of Palestinian goods and labor into Israel. These changes fueled an almost three-year-long economic recovery in the Gaza Strip. Recovery ended with the outbreak of the al-Aqsa Intifada in the last quarter of 2000. The al-Aqsa Intifada triggered tight IDF closures of the border with Israel, as well as frequent curbs on traffic in Palestinian self-rule areas, severely disrupting trade and labor movements. In 2001, and even more severely in early 2002, internal turmoil and Israeli military measures in Palestinian Authority areas resulted in the destruction of capital plant and administrative structure, widespread business closures, and a sharp drop in GDP. Another major factor has been the decline of income earned due to reduction in the number of Gazans permitted entry to work in Israel. After the Israeli withdrawal from Gaza, the flow of a limited number of workers into Israel again resumed, although Israel has stated its intention to reduce or end such permits due to the victory of Hamas in the 2006 parliamentary elections.
The Israeli settlers of Gush Katif built greenhouses and experimented with new forms of agriculture. These greenhouses also provided employment for many hundred Gazan Palestinians. When Israel withdrew from the Gaza Strip in the Summer of 2005, the greenhouses were purchased with money raised by former World Bank president James Wolfensohn, and given to the Palestinian people to jump-start their economy. However, the effort faltered due to limited water supply, inability to export produce due to Israeli border restrictions, and corruption in the Palestinian Authority. Most of the greenhouses were subsequently looted or destroyed.
According to the CIA World Factbook, GDP in 2001 declined 35% to a per capita income of $625 a year, and 60% of the population is now below the poverty line. Gaza Strip industries are generally small family businesses that produce textiles, soap, olive-wood carvings, and mother-of-pearl souvenirs; the Israelis have established some small-scale modern industries in an industrial centre. Israel supplies the Gaza Strip with electricity. The main agricultural products are olives, citrus, vegetables, Halal beef, and dairy products. Primary exports are citrus and cut flowers, while primary imports are food, consumer goods, and construction materials. The main trade partners of the Gaza Strip are Israel, Egypt, and the West Bank.
Before the second Palestinian uprising broke out in September 2000, around 25,000 workers from the Gaza Strip used to work in Israel every day.
Israel, the United States, Canada, and the European Union have frozen all funds to the Palestinian government after the formation of a Hamas-controlled government after its victory in the 2006 Palestinian legislative election. They view the group as a terrorist organization, and have pressured Hamas to recognize Israel, renounce violence, and agree to past agreements. Since Israel's withdrawal and its subsequent blockade, the gross domestic product of the Gaza Strip has been crippled. The enterprise and industry of the former Jewish villages has been impaired, and the previously established work relationships between Israel and the Gaza Strip have been disrupted. Job opportunities in Israel for Gaza Palestinians have been largely lost. Prior to disengagement, 120,000 Palestinians from Gaza were employed in Israel or in joint projects. Only about 20,000 have been able to keep these jobs.
After the seizure by Hamas militias of the Gaza Strip on 14 June 2007, all contact between the outside world and the Strip has been severed. The only goods permitted into the Strip through the land crossings are goods of a humanitarian nature.
Health
A study carried out by Johns Hopkins University (USA) and Al-Quds University (in Jerusalem) for CARE International in late 2002 revealed very high levels of dietary deficiency among the Palestinian population. The study found that 17.5% of children aged 6–59 months suffered from chronic malnutrition. 53% of women of reproductive age and 44% of children were found to be anaemia. In the aftermath of the Israeli withdrawal of August and September 2005, the healthcare system in Gaza continues to face severe challenges.After the Hamas takeover of the Gaza Strip and the subsequent Israeli declaration of Gaza Strip as a " hostile entity" , the health conditions in Gaza Strip faces new challenges exacerbated by the intensified Israeli closure. The WHO expressed its concerns about the consequences of the Palestinian internal political fragmentation; the socioeconomic decline; military actions; and the Physical, psychological and economic isolation on the health of the population in Gaza.
Transport and communication
The Gaza Strip has a small, poorly developed road network. It also had a single standard gauge railway line running the entire length of the Strip from north to south along its centre; however, it is abandoned, in disrepair, and little trackage remains. The line once connected to the Egyptian railway system to the south, as well as the Israeli system to the north.
The strip's one port was never completed after the outbreak of the al-Aqsa Intifada. Its airport, the Gaza International Airport, opened on 24 November 1998, as part of agreements stipulated in the Oslo II Accord and the 23 October 1998 Wye River Memorandum. The airport was closed in October 2000 by Israeli orders, and its runway was destroyed by the Israel Defense Forces in December 2001. It has since been renamed Yasser Arafat International Airport.
The Gaza Strip has rudimentary land line telephone service provided by an open-wire system, as well as extensive mobile telephone services provided by PalTel (Jawwal), or Israeli providers such as Cellcom. Gaza is serviced by four internet service providers that now compete for ADSL and dial-up customers. Most Gaza households have a radio and a TV (70%+), and approximately 20% have a personal computer. People living in Gaza have access to FTA satellite programs, broadcast TV from the Palestinian Broadcasting Corporation, the Israel Broadcasting Authority, and the Second Israeli Broadcasting Authority.