Boston, Massachusetts
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Cities; North America
| City of Boston | |||
|
|||
| Nickname: Beantown, The Hub (of the Solar System),1 The Cradle of Liberty, Title Town, The Cradle of Modern America, City on a Hill, Athens of America, The Walking City | |||
| Location in Suffolk County in Massachusetts, USA | |||
| Coordinates: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | United States | ||
| State | Massachusetts | ||
| County | Suffolk | ||
| Settled | 1630 | ||
| Incorporated (city) | 1822 | ||
| Government | |||
| - Mayor | Thomas M. Menino ( D) | ||
| Area | |||
| - City | 89.6 sq mi (232.1 km²) | ||
| - Land | 48.4 sq mi (125.4 km²) | ||
| - Water | 41.2 sq mi (106.7 km²) | ||
| - Metro | 4,511.5 sq mi (11,684.7 km²) | ||
| Elevation | 141 ft (43 m) | ||
| Population (2006) | |||
| - City | 590,763 | ||
| - Density | 12,327/sq mi (4,815/km²) | ||
| - Urban | 4,313,000 | ||
| - Metro | 4,455,217 | ||
| - Demonym | Bostonian | ||
| Time zone | Eastern ( UTC-5) | ||
| - Summer ( DST) | Eastern ( UTC-4) | ||
| Area code(s) | 617 / 857 | ||
| FIPS code | 25-07000 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 0617565 | ||
| 1 The State House, according to Oliver Wendell Holmes, is the hub of the Solar System | |||
| Website: www.cityofboston.gov | |||
Boston (pronounced /ˈbɒstən/ ) is the capital and largest city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The city is located in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. The largest city in New England, Boston is considered the economic and cultural centre of the entire region. The city, which had an estimated population of 590,763 in 2006, lies at the centre of the Cambridge–Boston-Quincy metropolitan area—the 10th-largest metropolitan area (5th largest CSA) in the U.S., with a population of 4.5 million.
In 1630, Puritan colonists from England founded the city on the Shawmut Peninsula. During the late eighteenth century Boston was the location of several major events during the American Revolution, including the Boston Massacre and the Boston Tea Party. Several early battles of the American Revolution, such as the Battle of Bunker Hill and the Siege of Boston, occurred within the city and surrounding areas. After American independence was attained Boston became a major shipping port and manufacturing centre, and its rich history now attracts 16.3 million visitors annually. The city was the site of several firsts, including America's first public school, Boston Latin School (1635), and first college, Harvard College (1636), in neighboring Cambridge. Boston was also home to the first subway system in the United States.
Through land reclamation and municipal annexation, Boston has expanded beyond the peninsula. With many colleges and universities within the city and surrounding area, Boston is a centre of higher education and a centre for medicine. The city's economy is also based on research, finance, and technology – principally biotechnology. Boston has been experiencing gentrification and has one of the highest costs of living in the United States, though remains high on world livability rankings.
History
Boston was founded on September 17, 1630 by Puritan colonists from England. The Puritans of the Massachusetts Bay Colony are sometimes confused with the Pilgrims who founded Plymouth Colony ten years earlier in what is today Bristol County, Plymouth County, and Barnstable County, Massachusetts. The two groups are historically distinct and differed in religious practice. The separate colonies were not united until the formation of the Province of Massachusetts Bay in 1691.
The Shawmut peninsula was connected to the mainland by a narrow isthmus, and surrounded by the waters of Massachusetts Bay and the Back Bay, an estuary of the Charles River. Several prehistoric Native American archaeological sites excavated in the city have shown that the peninsula was inhabited as early as 5,000 BC. Boston's early European settlers first called the area Trimountaine, but later renamed the town after Boston, Lincolnshire, England, from which several prominent colonists had emigrated. Massachusetts Bay Colony's original governor, John Winthrop, gave a famous sermon entitled " A Model of Christian Charity," popularly known as the "City on a Hill" sermon, which captured the idea that Boston had a special covenant with God. (Winthrop also led the signing of the Cambridge Agreement, which is regarded as a key founding document of the city.) Puritan ethics molded a stable and well-structured society in Boston. For example, shortly after Boston's settlement, Puritans founded America's first public school, Boston Latin School (1635), and America's first college, Harvard College (1636). Boston was the largest town in British North America until the mid-1700s.
In the 1770s, British attempts to exert more stringent control on the thirteen colonies, primarily via taxation, prompted Bostonians to initiate the American Revolution. The Boston Massacre, the Boston Tea Party, and several early battles occurred in or near the city, including the Battle of Lexington and Concord, Battle of Bunker Hill, and the Siege of Boston. During this period, Paul Revere made his famous midnight ride.
After the Revolution, Boston had become one of the world's wealthiest international trading ports due to the city's consolidated seafaring tradition – exports included rum, fish, salt, and tobacco. During this era, descendants of old Boston families became regarded as the nation's social and cultural elites; they were later dubbed the Boston Brahmins. In 1822, Boston was chartered as a city.
The Embargo Act of 1807, adopted during the Napoleonic Wars, and the War of 1812 significantly curtailed Boston's harbour activity. Although foreign trade returned after these hostilities, Boston's merchants had found alternatives for their capital investments in the interim. Manufacturing became an important component of the city's economy and by the mid-1800s, the city's industrial manufacturing overtook international trade in economic importance. Until the early 1900s, Boston remained one of the nation's largest manufacturing centers, and was notable for its garment production and leather goods industries. A network of small rivers bordering the city and connecting it to the surrounding region made for easy shipment of goods and allowed for a proliferation of mills and factories. Later, a dense network of railroads facilitated the region's industry and commerce. From the mid- to late nineteenth century, Boston flourished culturally; it became renowned for its rarefied literary culture and lavish artistic patronage. It also became a centre of the abolitionist movement. The city reacted strongly to the Fugitive Slave Law, which contributed to President Franklin Pierce's attempt to make an example of Boston after the Burns Fugitive Slave Case.
In the 1820s, Boston's population began to swell and the city's ethnic composition changed dramatically with the first wave of European immigrants. Irish immigrants dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period. By 1850, about 35,000 Irish lived in Boston. In the latter half of the nineteenth century, the city saw increasing numbers of Irish, Germans, Lebanese, French Canadians, and Russian and Polish Jews settle in the city. By the end of the nineteenth century, Boston's core neighborhoods had become enclaves of ethnically distinct immigrants – Italians inhabited the North End, the Irish dominated South Boston, and Russian Jews lived in the West End.
Irish and Italian immigrants brought with them Roman Catholicism. Currently, Catholics make up Boston's largest religious community and since the early twentieth century the Irish have played a major role in Boston politics—prominent figures include the Kennedys, Tip O'Neill, and John F. Fitzgerald.
Between 1630 and 1890, the city tripled its physical size by land reclamation, by filling in marshes, mud flats, and gaps between wharves along the waterfront, a process Walter Muir Whitehill called "cutting down the hills to fill the coves." The largest reclamation efforts took place during the 1800s. Beginning in 1807, the crown of Beacon Hill was used to fill in a 50- acre (20 ha) mill pond that later became Haymarket Square. The present-day State House sits atop this shortened Beacon Hill. Reclamation projects in the middle of the century created significant parts of the South End, West End, the Financial District and Chinatown. After The Great Boston Fire of 1872, workers used building rubble as landfill along the downtown waterfront. During the mid-to-late nineteenth century, workers filled almost 600 acres (2.4 km²) of brackish Charles River marshlands west of the Boston Common with gravel brought by rail from the hills of Needham Heights. In addition, the city annexed the adjacent towns of Roxbury (1868), Dorchester (1870), Brighton, West Roxbury (including present day Jamaica Plain, Roslindale and West Roxbury), and Charlestown. The last three towns were annexed in 1874.
The first community health center in the United States was the Columbia Point Health Centre in the Dorchester neighbourhood of Boston. It was opened in December 1965 and served mostly the massive Columbia Point public housing complex adjoining it. It was founded by two medical doctors, Jack Geiger of Harvard University and Count Gibson of Tufts University. It is still in operation and was re-dedicated in 1990 as the Geiger-Gibson Community Health Centre.
By the early and mid-twentieth century, the city was in decline as factories became old and obsolete, and businesses moved out of the region for cheaper labor elsewhere. Boston responded by initiating various urban renewal projects under the direction of the Boston Redevelopment Authority (BRA), which was established in 1957. In 1958, BRA initiated a project to improve the historic West End neighbourhood. Extensive demolition garnered vociferous public opposition to the new agency. BRA subsequently reevaluated its approach to urban renewal in its future projects, including the construction of Government Centre. By the 1970s, the city's economy boomed after thirty years of economic downturn. Hospitals such as Massachusetts General Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Centre, and Brigham and Women's Hospital led the nation in medical innovation and patient care. Schools such as Harvard University, MIT, Boston University, Boston College and Northeastern University attracted students to the Boston area. Nevertheless, the city experienced conflict starting in 1974 over desegregation busing, which resulted in unrest and violence around public schools throughout the mid-1970s.
The Columbia Point housing projects, built in 1953 on the Dorchester peninsula, had gone through bad times until there were only 350 families living in it in 1988. It was run down and dangerous. In 1984, the city of Boston gave control of it to a private developer, Corcoran-Mullins-Jennison, who re-developed and re-vitalised the property into an attractive residential mixed-income community called Harbour Point Apartments which was opened in 1988 and completed by 1990. It is a very significant example of revitalisation and re-development and was the first federal housing project to be converted to private, mixed-income housing in the United States.
In the early twenty-first century the city has become an intellectual, technological, and political centre. It has, however, experienced a loss of regional institutions, which included the acquisition of the Boston Globe by The New York Times, and the loss to mergers and acquisitions of local financial institutions such FleetBoston Financial, which was acquired by Charlotte-based Bank of America in 2004. The city also had to tackle gentrification issues and rising living expenses, with housing prices increasing sharply since the 1990s.
Geography
Owing to its early founding, Boston is very compact. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 89.6 square miles (232.1 km²)—48.4 square miles (125.4 km²) of it is land and 41.2 square miles (106.7 km²) (46.0%) of it is water. This compares with cities of comparable population such as Denver at 154.9 square miles (401 km²) and Charlotte, North Carolina at 280.5 square miles (726 km²). Of United States cities over 500,000 in population, only San Francisco is smaller in land area. Boston's official elevation, as measured at Logan International Airport, is 19 feet (5.8 m) above sea level. The highest point in Boston is Bellevue Hill at 330 feet (101 m) above sea level, while the lowest point is at sea level.
Boston is surrounded by the " Greater Boston" region, and bordered by the cities and towns of Winthrop, Revere, Chelsea, Everett, Somerville, Cambridge, Watertown, Newton, Brookline, Needham, Dedham, Canton, Milton, and Quincy.
Much of the Back Bay and South End neighborhoods are built on reclaimed land—all of the earth from two of Boston's three original hills, the "trimount", was used as landfill material. Only Beacon Hill, the smallest of the three original hills, remains partially intact; just half of its height was cut down for landfill. The downtown area and immediate surroundings consist mostly of low-rise brick or stone buildings, with many older buildings in the Federal style. Several of these buildings mix in with modern high-rises, notably in the Financial District, Government Centre, the South Boston waterfront, and Back Bay, which includes many prominent landmarks such as the Boston Public Library, Christian Science Centre, Copley Square, Newbury Street, and New England's two tallest buildings: the John Hancock Tower and the Prudential Centre. Near the John Hancock Tower is the old John Hancock Building with its prominent weather forecast beacon—whatever light illuminates gives an indication of weather to come: "steady blue. clear view; flashing blue, clouds are due; steady red, rain ahead; flashing red, snow instead." (In the summer, flashing red indicates instead that a Red Sox game has been rained out.) Smaller commercial areas are interspersed among single-family homes and wooden/brick multi-family row houses. Currently, the South End Historic District remains the largest surviving contiguous Victorian-era neighbourhood in the U.S.
Along with downtown, the geography of South Boston was particularly impacted by the Central Artery/Tunnel (CA/T) Project (or the "Big Dig"). The unstable reclaimed land in South Boston posed special problems for the project's tunnels. In the downtown area, the CA/T Project allowed for the removal of the unsightly elevated Central Artery and the incorporation of new green spaces and open areas.
Boston Common, located near the Financial District and Beacon Hill, is the oldest public park in the U.S. Along with the adjacent Boston Public Garden, it is part of the Emerald Necklace, a string of parks designed by Frederick Law Olmsted to encircle the city. Franklin Park, which is also part of the Emerald Necklace, is the city's largest park and houses a zoo. Another major park is the Esplanade located along the banks of the Charles River. Other parks are scattered throughout the city, with the major parks and beaches located near Castle Island, in Charlestown and along the Dorchester, South Boston, and East Boston shorelines.
The Charles River separates Boston proper from Cambridge, Watertown, and the neighbourhood of Charlestown. To the east lies Boston Harbour and the Boston Harbour Islands National Recreation Area. The Neponset River forms the boundary between Boston's southern neighborhoods and the city of Quincy and the town of Milton. The Mystic River separates Charlestown from Chelsea and Everett, while Chelsea Creek and Boston Harbour separate East Boston from Boston proper.
Cityscape
Climate
Boston has what may basically be described as a continental climate, such as is very common in New England. Summers are typically hot and humid, while winters are cold, windy and snowy. Prevailing wind patterns that blow offshore affect Boston, minimizing the influence of the Atlantic Ocean.
February in Boston has seen 70 ° F (21 ° C) only once in recorded history, on February 24, 1985. The maximum temperature recorded in March was 90 °F (32 °C), on March 31, 1998. Spring in Boston can be warm, with temperatures as high as the 90s when winds are offshore, though it is just as possible for a day in late May to remain in the lower 40s due to cool ocean waters. The hottest month is July, with an average high of 82 ° F (28 °C) and average low of 66 °F (18 °C), with conditions usually humid. The coldest month is January, with an average high of 36 °F (2 °C) and an average low of 22 °F (-6 °C). Periods exceeding 90 °F (32 °C) in summer and below 10 °F (−12 °C) in winter are not uncommon, but rarely prolonged. The record high temperature is 104 °F (40 °C), recorded July 4, 1911. The record low temperature is -18 °F (-28 °C), recorded on February 9, 1934.
The city averages about 42 in (108 cm) of precipitation a year, with 40.9 in (104 cm) of snowfall a year. Snowfall increases dramatically as one goes inland away from the city and the warming influence of the ocean. Most snowfall occurs December through March, usually with little or no snow in April and November and rare snow events in May and October.
Boston's coastal location on the North Atlantic, though it moderates temperatures, also makes the city very prone to Nor'easter weather systems that can produce much snow and rain. Fog is prevalent, particularly in spring and early summer, and the occasional tropical storm or hurricane can threaten the region, especially in early autumn.
| Weather averages for Boston, Massachusetts | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 36 (2) | 38 (3) | 45 (7) | 56 (13) | 67 (19) | 77 (25) | 82 (28) | 80 (27) | 73 (23) | 63 (17) | 52 (11) | 41 (5) | 59 (15) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 22 (-6) | 23 (-5) | 31 (-1) | 40 (4) | 50 (10) | 59 (15) | 65 (18) | 64 (18) | 57 (14) | 47 (8) | 38 (3) | 27 (-3) | 44 (7) |
| Precipitation inches (mm) | 3.8 (97) | 3.5 (89) | 4.0 (102) | 3.7 (94) | 3.4 (86) | 3.0 (76) | 2.8 (71) | 3.6 (91) | 3.3 (84) | 3.3 (84) | 4.4 (112) | 4.2 (107) | 42.9 (1,090) |
| Source: Weatherbase Feb 2007 | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 18,320 |
|
|
| 1800 | 24,937 | 36.1% | |
| 1810 | 33,787 | 35.5% | |
| 1820 | 43,298 | 28.1% | |
| 1830 | 61,392 | 41.8% | |
| 1840 | 93,383 | 52.1% | |
| 1850 | 136,881 | 46.6% | |
| 1860 | 177,840 | 29.9% | |
| 1870 | 250,526 | 40.9% | |
| 1880 | 362,839 | 44.8% | |
| 1890 | 448,477 | 23.6% | |
| 1900 | 560,892 | 25.1% | |
| 1910 | 670,585 | 19.6% | |
| 1920 | 748,060 | 11.6% | |
| 1930 | 781,188 | 4.4% | |
| 1940 | 770,816 | −1.3% | |
| 1950 | 801,444 | 4% | |
| 1960 | 697,197 | −13% | |
| 1970 | 641,071 | −8.1% | |
| 1980 | 562,994 | −12.2% | |
| 1990 | 574,283 | 2% | |
| 2000 | 589,141 | 2.6% | |
| Est. 2006 | 590,763 | 0.3% | |
According to the census of 2000, there were 589,141 people, (the population estimate of 2006 was 596,638 people), 239,528 households, and 115,212 families residing in the city. The population density was 12,166 people per square mile (4,697/km²). Of major US cities, only New York City, San Francisco, and Chicago have a greater population density than Boston. There were 251,935 housing units at an average density of 5,203 per square mile (2,009/km²).
However, the population of Boston can grow during the daytime to about 1.2 million. This fluctuation of people is caused by suburban residents traveling to the city for work, education, medical purposes, and special events.
According to the 2000 census, the racial makeup of the city was 49% Non-Hispanic White, 25% African American or Black, 8% Asian American, 1% Native American, 4% from other races, and 3% from two or more races. 14% of the population was Hispanic or Latino who can be of any race.
According to a 2006 estimate, the White population comprises 53.5% of the population, while Hispanics make up 15.5%. People of Irish descent form the largest single ethnic group in the city, making up 15.8% of the population, followed by Italians, accounting for 8.3% of the population. People of West Indian ancestry are another sizeable group, at 6.4%, about half of whom are of Haitian ancestry. Some neighborhoods, such as Dorchester, have received an influx of Vietnamese residents in recent decades. Neighborhoods such as Jamaica Plain and Roslindale have experienced a growing number of Dominican Americans.
There were 239,528 households, out of which 22.7% had children under the age of 18 living in them, 27.4% were married couples living together, 16.4% had a female householder with no husband present, and 51.9% were non-families. 37.1% of all households were made up of individuals and 9.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.31 and the average family size was 3.17.
In the city the population was spread out with 19.8% under the age of 18, 16.2% from 18 to 24, 35.8% from 25 to 44, 17.8% from 45 to 64, and 10.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 31 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.2 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $39,629, and the median income for a family was $44,151. Males had a median income of $37,435 versus $32,421 for females. The per capita income for the city was $23,353. 19.5% of the population and 15.3% of families are below the poverty line. Out of the total population, 25.6% of those under the age of 18 and 18.2% of those 65 and older were living below the poverty line.
Government
Boston has a strong mayor system in which the mayor is vested with extensive executive powers. The mayor is elected to a four-year term by plurality voting. The city council is elected every two years. There are nine district seats, each elected by the residents of that district through plurality voting, and four at-large seats. Each voter casts up to four votes for at-large councilors, with no more than one vote per candidate. The candidates with the four highest vote totals are elected. The president of the city council is elected by the councilors from within themselves. The school committee for the Boston Public Schools is appointed by the mayor. The Boston Redevelopment Authority and the Zoning Board of Appeals (a seven-person body appointed by the mayor) share responsibility for land-use planning.
In addition to city government, numerous state authorities and commissions play a role in the life of Bostonians, including the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation and the Massachusetts Port Authority (Massport). As the capital of Massachusetts, Boston plays a major role in state politics. The city has several properties relating to the United States federal government, including the John F. Kennedy Federal Office Building and the Thomas P. O'Neill Federal Building. The city also serves as the home of the United States Court of Appeals for the First Circuit, the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts, as well as the headquarters of the Federal Reserve Bank of Boston (the First District of the Federal Reserve). The city is in the Eighth and Ninth Congressional districts.
Crime
The city has seen a great reduction in violent crime since the early 1990s. Boston's low crime rate in the last years of the twentieth century and the beginning of the twenty-first has been credited to its police department's collaboration with neighbourhood groups and church parishes to prevent youths from joining gangs, as well as involvement from the United States Attorney and District Attorney's offices. This helped lead in part to what has been touted as the "Boston Miracle." Murders in the city dropped from 152 in 1990 (for a murder rate of 26.5 per 100,000 people) to just 31—not one of them a juvenile—in 1999 (for a murder rate of 5.26 per 100,000). In more recent years, however, the annual murder count has fluctuated by as much as 50% compared to the year before, with 60 murders in 2002, followed by just 39 in 2003, 64 in 2004, and 75 in 2005. Though the figures are nowhere near the high-water mark set in 1990, the aberrations in the murder rate have been unsettling for many Bostonians and have prompted discussion over whether the Boston Police Department should reevaluate its approach to fighting crime.
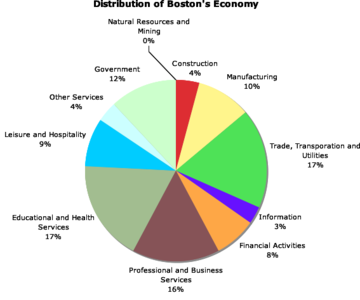
Economy
Boston's colleges and universities have a major impact on the city and region's economy. Not only are they major employers, but they also attract high-tech industries to the city and surrounding region. Boston is home to technology companies such as EMC Corp. and Analog Devices as well as E-Commerce companies VistaPrint and CSN Stores. Boston is also a major hub for biotechnology companies, including Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co., Millipore, Genzyme, and Biogen Idec. According to a 2003 report by the Boston Redevelopment Authority, students enrolled in Boston's colleges and universities contribute $4.8 billion annually to the city's economy. Boston also receives the highest amount of annual funding from the National Institutes of Health of all cities in the United States.
Tourism comprises a large part of Boston's economy. In 2004 tourists spent $7.9 billion and made the city one of the ten most popular tourist locations in the country. Other important industries include financial services, especially mutual funds and insurance. Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped popularize the mutual fund in the 1980s, and has made Boston one of the top financial cities in the United States. The city is also the regional headquarters of major banks such as Bank of America and Sovereign Bank, and a centre for venture capital. State Street Corporation, which specializes in asset management and custody services, is headquartered in the city. Boston is also a printing and publishing centre – Houghton Mifflin is headquartered within the city, along with Bedford-St. Martin's Press, Beacon Press, and Little, Brown and Company. Pearson PLC publishing units also employ several hundred people in Boston. The city is home to four major convention centers: the Hynes Convention Centre in the Back Bay, the Bayside Expo Center in Dorchester, and the World Trade Centre Boston and Boston Convention and Exhibition Centre on the South Boston waterfront. Because of its status as a state capital and the regional home of federal agencies, law and government is another major component of the city's economy.
Major companies headquartered within the city include the Liberty Mutual insurance company, Gillette (now owned by Procter & Gamble), and Teradyne, one of the world's leading manufacturers of semiconductor and other electronic test equipment. New Balance has its headquarters in the city. Boston is also home to management consulting firms The Boston Consulting Group, Monitor Group, and Bain & Company, as well as the private equity group Bain Capital. Other major companies are located outside the city, especially along Route 128. The Port of Boston is a major seaport along the United States' East Coast, and is also the oldest continuously-operated industrial and fishing port in the Western Hemisphere. Boston is classified as a " Gamma world city" by a study group at Loughborough University in England.
Education
Boston's reputation as the Athens of America derives in large part from the teaching and research activities of more than 100 colleges and universities located in the Greater Boston Area, with more than 250,000 students attending college in Boston and Cambridge alone. Within the city, Boston University exudes a large presence as the city's fourth-largest employer, and maintains a campus along the Charles River on Commonwealth Avenue and its medical campus in the South End. Northeastern University, another large private university, is located in the Fenway area, and is particularly known for its Business and Health Science schools and cooperative education program. Wheelock College, Massachusetts College of Art and Design, Simmons College, Emmanuel College, Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, and Wentworth Institute of Technology, founding members of the Colleges of the Fenway, are adjacent to Northeastern University. Suffolk University, a small private university known for its law school, maintains a campus on Beacon Hill. New England School of Law, a small private law school located in the theatre district, was originally established as America's only all female law school. Emerson College, a small private college with a strong reputation in the fields of performing arts, journalism, writing, and film, is located nearby on Boston Common. Boston College, whose original campus was located in South Boston, moved its campus west to a site that straddles the Boston(Brighton)-Newton border. Boston College is expanding further into the Brighton neighbourhood following the purchase of adjacent land from the Boston Catholic Archdiocese.
Boston is also home to several conservatories and art schools, including the Art Institute of Boston, Massachusetts College of Art, and the New England Conservatory of Music (the oldest independent conservatory in the United States). Other conservatories include the Boston Conservatory, the School of the Museum of Fine Arts and Berklee College of Music. Boston has one major public university, the University of Massachusetts Boston, located on Columbia Point in Dorchester, while Roxbury Community College and Bunker Hill Community College are the city's two community colleges.
Several major national universities located outside Boston have a major presence in the city. Harvard University, the nation's oldest, and arguably best known, institution of higher learning, is located across the Charles River in Cambridge. The business and medical schools are in Boston, and there are plans for additional expansion into Boston's Allston neighbourhood. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), which originated in Boston and was long known as " Boston Tech," moved across the river to Cambridge in 1916. Tufts University administers its medical and dental school adjacent to the Tufts Medical Centre, a 451-bed academic medical institution that is home to both a full-service hospital for adults and the Floating Hospital for Children. Eastern Nazarene College in Quincy, is the only evangelical Christian college in metropolitan Boston and is active in Christian ministry in the City of Boston.
Boston Public Schools, the oldest public school system in the U.S., enrolls 57,000 students from kindergarten to grade 12. The system operates 145 schools, which includes Boston Latin School (the oldest public school in the United States, established in 1635; which, along with Boston Latin Academy, is a highly prestigious public exam school admitting students in the 7th and 9th grades only and serving grades 7–12), English High (the oldest public high school, established 1821), and the Mather School (the oldest public elementary school, established in 1639). The city also has private, parochial, and charter schools. 3000 students of racial minorities attend participating suburban schools through the Metropolitan Educational Opportunity Council, or METCO. In 2002, Forbes Magazine ranked the Boston Public Schools as the best large city school system in the country, with a graduation rate of 82%. In 2005, the student population within the school system was 45.5% Black or African American, 31.2% Hispanic or Latino, 14% White, and 9% Asian, as compared with 24%, 14%, 49%, and 8% respectively for the city as a whole.
Culture
Boston shares many cultural roots with greater New England, including a dialect of the non- rhotic Eastern New England accent known as Boston English, and a regional cuisine with a large emphasis on seafood, rum, salt, and dairy products. Irish Americans are a major influence on Boston's politics and religious institutions. Boston also has its own collection of neologisms known as Boston slang.
Many consider Boston to have a strong sense of cultural identity, perhaps as a result of its intellectual reputation; much of Boston's culture originates at its universities. The city has several ornate theatres, including the Cutler Majestic Theatre, Boston Opera House, Citi Performing Arts Centre, and the Orpheum Theatre. Renowned performing arts organizations include the Boston Symphony Orchestra, Boston Ballet, Boston Pops, Celebrity Series of Boston, Boston Early Music Festival, Boston Lyric Opera Company, OperaBoston, Emmanuel Music, and the Handel and Haydn Society (one of the oldest choral companies in the United States). There are also many major annual events such as First Night, which occurs during New Year's Eve, Italian summer feasts in the North End honoring Catholic saints, and several events during the Fourth of July. These events include the week-long Harborfest festivities and a Boston Pops concert accompanied by fireworks on the banks of the Charles River.
Because of the city's prominent role in the American Revolution, several historic sites relating to that period are preserved as part of the Boston National Historical Park. Many are found along the Freedom Trail, which is marked by a red line or bricks embedded in the ground. The city is also home to several prominent art museums, including the Museum of Fine Arts and the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum. In December 2006 the Institute of Contemporary Art moved from its Back Bay location to a new contemporary building designed by Diller Scofidio + Renfro located in the Seaport District. The University of Massachusetts campus at Columbia Point houses the John F. Kennedy Library. The Boston Athenaeum (one of the oldest independent libraries in the United States), Boston Children's Museum, Bull & Finch Pub (whose building is known from the television show Cheers), Museum of Science, and the New England Aquarium are within the city.
Boston is also one of the birthplaces of the hardcore punk genre of music. Boston musicians have contributed greatly to this music scene over the years (see also Boston hardcore). Boston neighborhoods were home to one of the leading local third wave ska and ska punk scenes in the 1990s, led by bands such as The Mighty Mighty Bosstones, The Allstonians, Skavoovie and the Epitones, and the Dropkick Murphys. The 1980s hardcore punk rock compilation This Is Boston, Not L.A. highlights some of the bands that built the genre. Several nightclubs, such as The Channel, Bunnratty's in Allston, and The Rathskeller, were renowned for showcasing both local punk rock bands and those from farther afield. All of these clubs are now closed, and in many cases razed during recent gentrification.
Sports
The Boston Red Sox are a founding member of the American League of Major League Baseball and are the 2007 World Series champions. The team plays its home games at Fenway Park, near Kenmore Square in the Fenway section. Built in 1912, it is the oldest sports arena or stadium in active use in the United States among the four major professional sports. Boston was also the site of the first game of the first modern World Series, in 1903. The series was played between the Red Sox and the Pittsburgh Pirates. Persistent reports that the team was known in 1903 as the "Boston Pilgrims" appear to be unfounded. The Boston Braves were Boston's NL team (1871-1953) until they moved to Milwaukee in 1953, then later Atlanta in 1966 where they currently play as the Atlanta Braves.
The TD Banknorth Garden (formerly called the Fleet Center, and the Shawmut Centre) is adjoined to North Station and is the home of two major league teams: the Boston Bruins ice hockey team of the National Hockey League and the 2008 National Basketball Association champions, the Boston Celtics. The Bruins were the first American member of the National Hockey League and an Original Six franchise. The Boston Celtics were founding members of the Basketball Association of America, one of the two leagues that merged to form the NBA. The Celtics have the distinction of having more national titles than any other NBA team with 17 championships from 1957 to 2008.
Although the team has played in suburban Foxboro since 1971, the New England Patriots are Boston's football team. The team was founded in 1960 as the Boston Patriots, a charter member of the American Football League, and in 1970 the team joined the National Football League. The team has won three Super Bowl titles since the 2001 season (in 2001, 2003, and 2004). They share Gillette Stadium with the New England Revolution of Major League Soccer. There has also been talk of a possible Arena Football League expansion team coming to Boston sometime in the next few years.
Boston's many colleges and universities are active in college athletics. There are four NCAA Division I members in the city: Boston College (member of the Atlantic Coast Conference), Boston University ( America East Conference), Northeastern University ( Colonial Athletic Association), and Harvard University ( Ivy League). All except Harvard, which belongs to ECAC Hockey, belong to the Hockey East conference. The hockey teams of these four universities meet every year in a four-team tournament known as the " Beanpot Tournament," which is played at the TD Banknorth Garden over two Monday nights in February.
One of the most famous sporting events in the city is the Boston Marathon, the 26.2 mile (42.2 km) run from Hopkinton to Copley Square in the Back Bay. The Marathon, the world's oldest, is popular and heavily attended. It is run on Patriots' Day in April and always coincides with a Red Sox home baseball game that starts at 11:05 AM (10:05 beginning in 2007), the only MLB game all year to start before noon local time. Another major event held in the city is the Head of the Charles Regatta rowing competition on the Charles River.
| Club | League | Sport | Venue | Established | Championships |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boston Red Sox | MLB | Baseball | Fenway Park | 1901 | 7 World Series Titles 12 AL Pennants |
| New England Patriots | NFL | Football | Gillette Stadium | 1960 | 3 Super Bowl Titles |
| Boston Celtics | NBA | Basketball | TD Banknorth Garden | 1946 | 17 NBA Titles |
| Boston Bruins | NHL | Hockey | TD Banknorth Garden | 1924 | 5 Stanley Cups |
| New England Revolution | MLS | Soccer | Gillette Stadium | 1995 | 1 U.S. Open Cup |
| Boston Cannons | MLL | Lacrosse (Outdoor) | Harvard Stadium | 2001 | None |
| Boston Blazers | NLL | Lacrosse (Indoor) | TD Banknorth Garden | 2008 | None |
| New England Riptide | NPF | Softball | Martin Softball Field | 2004 | 1 Cowles Cup |
Healthcare and utilities
The Longwood Medical Area is a region of Boston with a concentration of medical and research facilities, including Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Centre, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Children's Hospital Boston, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Harvard School of Public Health and Harvard School of Dental Medicine. Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) is near the Beacon Hill neighbourhood, with the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital nearby. Boston also has VA medical centers in the Jamaica Plain and West Roxbury neighborhoods.
Many of Boston's major medical facilities are associated with universities. The facilities in the Longwood Medical Area and MGH are world-renowned research medical centers affiliated with Harvard Medical School. Tufts Medical Centre (formerly Tufts-New England Medical Center), located in the southern portion of the Chinatown neighbourhood, is affiliated with Tufts University School of Medicine. Boston Medical Centre, located in the South End neighbourhood, is the primary teaching facility for the Boston University School of Medicine as well as the largest trauma centre in the Boston area; it was formed by the merger of Boston University Hospital and Boston City Hospital, which was the first municipal hospital in the U.S.
Water supply and sewage-disposal services are provided by the Boston Water and Sewer Commission. The Commission in turn purchases wholesale water and sewage disposal from the Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA). The city's water comes from the Quabbin Reservoir and the Wachusett Reservoir, which are about 65 miles (105 km) and 35 miles (56 km) west of the city respectively. NSTAR is the exclusive distributor of electric power to the city, though due to deregulation, customers now have a choice of electric generation companies. Natural gas is distributed by KeySpan Corporation (the successor company to Boston Gas); only commercial and industrial customers may choose an alternate natural gas supplier.
Verizon, successor to New England Telephone, NYNEX, Bell Atlantic and earlier, the Bell System, is the primary wired telephone service provider for the area. Phone service is also available from various national wireless companies. Cable television is available from Comcast and RCN, with Broadband Internet access provided by the same companies in certain areas. A variety of DSL providers and resellers are able to provide broadband Internet over Verizon-owned phone lines.
Transportation
Logan International Airport, located in the East Boston neighbourhood, handles most of the scheduled passenger service for Boston. Surrounding the city are three major general aviation relievers: Beverly Municipal Airport to the north, Hanscom Field in Bedford, to the west, and Norwood Memorial Airport to the south. T. F. Green Airport serving Providence, Rhode Island, and Manchester-Boston Airport in Manchester, New Hampshire, also provide scheduled passenger service to the Boston area.
Downtown Boston's streets are not organized on a grid, but grew in a meandering organic pattern beginning early in the seventeenth century. They were created as needed, and as wharves and landfill expanded the area of the small Boston peninsula. Along with several rotaries, roads change names and lose and add lanes seemingly at random. On the other hand, streets in the Back Bay, East Boston, the South End, and South Boston do follow a grid system.
Boston is the eastern terminus of I-90, which in Massachusetts runs along the Mass Pike. I-95, which surrounds the city, is locally referred to as Route 128, its historical state route numbering. U.S. Route 1 and I-93 and Massachusetts Route 3 run north to south through the city forming the elevated Central Artery, which ran through downtown Boston and was constantly prone to heavy traffic, was replaced with an underground tunnel through the Big Dig.
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) operates what was the first underground rapid transit system in the United States and is now the fourth busiest rapid transit system in the country, having been expanded to 65.5 miles (105 km) of track, reaching as far north as Malden, as far south as Braintree, and as far west as Newton – collectively known as the "T". The MBTA also operates the nation's sixth busiest bus network, as well as water shuttles, and a commuter rail network totaling over 200 miles (321 km), extending north to the Merrimack Valley, west to Worcester, and south to Providence. Nearly a third of Bostonians use public transit for their commute to work. Walking has a larger transit role in Boston than comparably populated cities. Owing to factors such as the compactness of the city and large student population, 13% of the population commutes by foot, making it the highest percentage of pedestrian commuters in the country out of the major American cities. In its March 2006 issue, Bicycling magazine named Boston as one of the worst cities in the U.S. for cycling; regardless, it has one of the highest rates of bicycle commuting.
Amtrak's Northeast Corridor and Chicago lines originate at South Station and stop at Back Bay. Fast Northeast Corridor trains, which service New York City, Washington, D.C., and points in between, also stop at Route 128 Station in the southwestern suburbs of Boston. Meanwhile, Amtrak's Downeaster service to Maine originates at North Station.