Abkhazia
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Asia; Asian Countries
| Аҧсны აფხაზეთი Абхазия Apsny / Apkhazeti / Abhazia Abkhazia
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
|
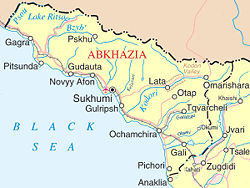
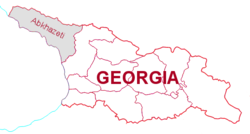
Location of Abkhazia (dark green, circled)
within Georgia (lighter green) |
||
| Area | ||
| - | Total | 8,432 km² 3,256 sq mi |
| - | Water (%) | negligible |
| Population | ||
| - | 2006 estimate | 157,000-190,000 ( International Crisis Group) 177,000 (Encyclopædia Britannica) |
| - | 2003 census | 216,000 (disputed) |
| - | Density | 29/km² 75.1/sq mi |
| Time zone | MSK ( UTC+3) | |
|
Republic of Abkhazia
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: " Aiaaira" (English "Victory") |
||||||
| Capital | Sukhumi |
|||||
| Official languages | Abkhaz, Russian1 | |||||
| Government | ||||||
| - | President | Sergei Bagapsh | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Alexander Ankvab | ||||
| De facto independence from Georgia | ||||||
| - | Declared | 23 July 1992 | ||||
| - | Recognition | none | ||||
| Currency | Russian ruble ( RUB) |
|||||
| 1 | Russian has co-official status and widespread use by government and other institutions. | |||||
|
Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: " თავისუფლება" "Freedom" |
||||||
|
Location of Abkhazia
within Georgia |
||||||
| Capital | Sukhumi (de jure) Chkhalta (de facto) |
|||||
| Official languages | Abkhaz, Georgian | |||||
| Government | ||||||
| - | Chairman, Cabinet of Ministers |
Malkhaz Akishbaia |
||||
| - | Chairman, Supreme Council | Temur Mzhavia | ||||
| Autonomous republic of Georgia | ||||||
| - | Georgian independence from the Soviet Union Declared
Recognised |
9 April 1991 25 December 1991 |
||||
| Currency | Georgian lari ( GEL) |
|||||
Abkhazia (pronounced /æbˈkeɪʒə/ or /æbˈkɑːziə/, Abkhaz: Аҧсны Apsny, Georgian: აფხაზეთი Apkhazeti or Abkhazeti, Russian: Абха́зия Abhazia) is a region in Georgia that is a de facto independent republic, with no international recognition. It is located within the internationally recognized borders of Georgia on the eastern coast of the Black Sea and borders the Russian Federation to the north. Under Georgia's official subdivision, it is an autonomous republic ( Georgian: აფხაზეთის ავტონომიური რესპუბლიკა, Abkhaz: Аҧснытәи Автономтәи Республика), with Sukhumi as its capital, bordering the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti to the east.
A secessionist movement of the Abkhaz ethnic minority in the region led to the declaration of independence from Georgia in 1992 and the Georgian-Abkhaz armed conflict from 1992 to 1993 which resulted in the Georgian military defeat and the mass exodus and ethnic cleansing of Georgian population from Abkhazia. In spite of the 1994 ceasefire accord and the ongoing UN-monitored and Russian-dominated CIS peacekeeping operation, the sovereignty dispute has not yet been resolved and the region remains divided between the two rival authorities, with over 83 percent of its territory governed by the Russian-backed Sukhumi-based separatist government and about 17 percent governed by the Government of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia, recognized by Georgia as the legal authority of Abkhazia, located in the Kodori Valley, part of Georgian-controlled Upper Abkhazia. This dispute remains a source of serious tension between Georgia and Russia.
Political status
The international organizations such as United Nations ( 28 Security Council Resolutions), EU, OSCE, NATO, WTO, Council of the European Union, CIS as well as most sovereign states recognize Abkhazia as an integral part of Georgia and support its territorial integrity according to the principles of the international law. The United Nations are urging both sides to settle the dispute through diplomatic dialogue and ratifying the final status of Abkhazia in the Georgian constitution. However, the Abkhaz de-facto government considers Abkhazia a sovereign country, even though it is not recognized by any party in the world and is still populated with ethnic Georgians (who live in the Gali District and the Kodori Gorge). In early 2000, then-U.N. Special Representative of the Secretary General Dieter Boden and the Group of Friends of Georgia, consisting of the representatives of Russia, the United States, Britain, France, and Germany, drafted and informally presented a document to the parties outlining a possible distribution of competencies between the Abkhaz and Georgian authorities, based on a core respect for Georgian territorial integrity. The Abkhaz side, however, has never accepted the paper as a basis for negotiations. Eventually, Russia also withdrew its approval of the document. In 2005 and 2008, the Georgian government offered Abkhazia a high degree of autonomy and possible federal structure within the borders and jurisdiction of Georgia.
However, the Russian State Duma is urging to take into consideration the appeal made by the Abkhaz Republic of Abkhazia which calls for recognition of its independence, and the Russian state media has produced numerous materials in support of the unrecognized state. During the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict, Russian authorities and military supplied logistical and military aid to the separatist side. Today, Russia still maintains a strong political and military influence over separatist rule in Abkhazia. Russia has also issued passports for the citizens of Abkhazia since 2000 (as the Abkhazian passports cannot be used for international travel) and subsequently paid retirement pensions and other monetary benefits. More than 80% of the Abkhazian population received Russian citizenship by 2006; however, Abkhazians do not pay Russian taxes, or serve in the Russian Army. About 53,000 Abkhazian passports have been issued as of May 2007.
On October 18, 2006, the People's Assembly of Abkhazia passed a resolution, calling upon Russia, international organizations, and the rest of the international community to recognize Abkhaz independence on the basis that Abkhazia possesses all the properties of an independent state. The United Nations has reaffirmed "the commitment of all Member States to the sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity of Georgia within its internationally recognized borders" and outlined the basic principles of conflict resolution which call for immediate return of all displaced persons and for non-resumption of hostilities. Of about 200,000-240,000, some 60,000 Georgian refugees spontaneously returned to Abkhazia's Gali district between 1994 and 1998, but tens of thousands were displaced again when fighting resumed in the Gali district in 1998. Nevertheless from 40,000 to 60,000 refugees have returned to the Gali district since 1998, including persons commuting daily across the ceasefire line and those migrating seasonally in accordance with agricultural cycles. The human rights situation remains precarious in the Georgian-populated areas of the Gali district. The United Nations and other international organizations have been fruitlessly urging the Abkhaz de facto authorities "to refrain from adopting measures incompatible with the right to return and with international human rights standards, such as discriminatory legislation... [and] to cooperate in the establishment of a permanent international human rights office in Gali and to admit United Nations civilian police without further delay." Key officials of the Gali district are virtually all ethnic Abkhaz, though their support staff are ethnic Georgian.
Georgia accuses the Abkhaz secessionists of having conducted a deliberate campaign of ethnic cleansing, a claim supported by the OSCE (Budapest, Lisbon and Istanbul declaration), United Nations (General Assembly Resolution 10708) and many Western governments. The UN Security Council has avoided use of the term "ethnic cleansing" but has affirmed "the unacceptability of the demographic changes resulting from the conflict". On May 15, 2008 United Nations General Assembly adopted a non-binding resolution recognising the right of all refugees (including victims of reported “ethnic cleansing”) to return to Abkhazia and their property rights. It "regretted" the attempts to alter pre-war demographic composition and called for the "rapid development of a timetable to ensure the prompt voluntary return of all refugees and internally displaced persons to their homes."
On March 28, 2008, the President of Georgia Mikheil Saakashvili unveiled his government's new proposals to Abkhazia: the broadest possible autonomy within the framework of a Georgian state, a joint free economic zone, representation in the central authorities including the post of vice-president with the right to veto Abkhaz-related decisions. The Abkhaz leader Sergei Bagapsh rejected these new initiatives as "propaganda", leading to Georgia's complaints that this skepticism was "triggered by Russia, rather than by real mood of the Abkhaz people."
Moscow, at certain times, had hinted that it might recognize Abkhazia and South Ossetia when the Western countries recognized the independence of Kosovo suggesting it created a precedent. Following Kosovo's declaration of independence the Russian parliament released a joint statement reading: "Now that the situation in Kosovo has become an international precedent, Russia should take into account the Kosovo scenario...when considering ongoing territorial conflicts." So far Russia has not recognised either of these republics. On April 16, 2008, the outgoing Russian president Vladimir Putin instructed his government to establish official ties with counterpart agencies in breakaway South Ossetia and Abkhazia, leading to Georgia's condemnation of what is described an attempt at "de facto annexation" and criticism from the European Union, NATO, and several Western governments.
Later in April 2008, Russia accused Georgia of trying to exploit the NATO support to solve the Abkhazia problem by force, and announced it would increase its military in the region, pledging to retaliate militarily to Georgia’s efforts. The Georgian Prime Minister Lado Gurgenidze has said Georgia will to treat any additional troops in Abkhazia as aggressors.
On July 3, 2008, the OSCE Parliamentary Assembly passed a resolution at its annual session in Astana, expressing concern over Russia’s recent moves in breakaway Abkhazia. The resolution calls on the Russian authorities to refrain from maintaining ties with the breakaway regions “in any manner that would constitute a challenge to the sovereignty of Georgia” and also urges Russia “to abide by OSCE standards and generally accepted international norms with respect to the threat or use of force to resolve conflicts in relations with other participating States.”
Geography and climate
Abkhazia covers an area of about 8,600 km² at the western end of Georgia. The Caucasus Mountains to the north and the northeast divide Abkhazia from the Russian Federation. To the east and southeast, Abkhazia is bounded by the Georgian region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti; and on the south and southwest by the Black Sea.
Abkhazia is extremely mountainous. The Greater Caucasus Mountain Range runs along the region's northern border, with its spurs – the Gagra, Bzyb and Kodori ranges – dividing the area into a number of deep, well-watered valleys. The highest peaks of Abkhazia are in the northeast and east and several exceed 4,000 meters (13,120 ft) above sea level. The landscapes of Abkhazia range from coastal forests and citrus plantations, to eternal snows and glaciers to the north of the region. Although Abkhazia's complex topographic setting has spared most of the territory from significant human development, its cultivated fertile lands produce tea, tobacco, wine and fruits, a mainstay of the local agricultural sector.
Abkhazia is richly irrigated by small rivers originating in the Caucasus Mountains. Chief of these are: Kodori, Bzyb, Ghalidzga, and Gumista. The Psou River separates the region from Russia, and the Inguri serves as a boundary between Abkhazia and Georgia proper. There are several periglacial and crater lakes in mountainous Abkhazia. Lake Ritsa is the most important of them.
Because of Abkhazia's proximity to the Black Sea and the shield of the Caucasus Mountains, the region's climate is very mild. The coastal areas of the republic have a subtropical climate, where the average annual temperature in most regions is around 15 degrees Celsius. The climate at higher elevations varies from maritime mountainous to cold and summerless. Abkhazia receives high amounts of precipitation, but its unique micro-climate (transitional from subtropical to mountain) along most of its coast causes lower levels of humidity. The annual precipitation vacillates from 1,100-1,500 mm (43-59 inches) along the coast to 1,700-3,500 mm (67-138 in.) in the higher mountainous areas. The mountains of Abkhazia receive significant amounts of snow.
There are two border crossings into Abkhazia. The southern border crossing is at the Inguri bridge, a short distance from the Georgian city of Zugdidi. The northern crossing ("Psou") is in the town of Gyachrypsh. Owing to the ongoing security situation, many foreign governments advise their citizens against travelling to Abkhazia.
Administrative division
In Soviet times Abkhaz ASSR was divided into 6 raions named after their centres: Gagra, Gudauta, Sukhumi, Ochamchira, Gulripsh and Gali. The de jure division of Abkhazian Autonomous Republic of Georgia remained the same (see here).
The administrative division of the unrecognised Republic of Abkhazia is the same with one exception - a new Tkvarcheli raion was carved from the Ochamchire and Gali raions in 1995.
Economy
The economy of Abkhazia is heavily integrated with Russia and uses the Russian ruble as its currency. Tourism is a key industry and the Abkhaz de facto authorities claim that the organized tourists (mainly from Russia) numbered more than 100,000 in recent years, compared to about 200,000 in the 1990 before the war. The number of visitors in 2006 was estimated by Abkhazian authorities to have been approximately 1.5 million. Although Russia has established a visa regime with Georgia, Russian passport-holders do not require a visa to enter Abkhazia. Holders of European Union passports require an Entry Permit Letter issued by the de facto Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Sukhumi, against which a visa will be issued upon presentation of the Letter to the MFA.
Abkhazia's fertile land and abundance of agricultural products, including tea, tobacco, wine and fruits (especially tangerines), have secured a relative stability in the sector. Electricity is largely supplied by the Inguri hydroelectric power station located on the Inguri River between Abkhazia and Georgia proper and operated jointly by Abkhaz and Georgians.
The exports and imports in 2006 were 627.2 and 3270.2 mln. rubles respectively (appx. 22 and 117 mln. US dollars) according to the Abkhazian authorities.
Many Russian entrepreneurs and some Russian municipalities have invested or plan to invest in Abkhazia. This includes the Moscow municipality after the Mayor of Moscow, Yury Luzhkov, signed an agreement on economic cooperation between Moscow and Abkhazia. Both Abkhaz and Russian officials have announced their intentions to exploit Abkhazia's facilities and resources for the Olympic construction projects in Sochi, as the city will host the 2014 Winter Olympics. The Government of Georgia has warned against such actions, however , and has threatened to ask foreign banks to close accounts of Russian companies and individuals that buy assets in Abkhazia.
According to the U.S.-based organization Freedom House, the region continues to suffer considerable economic problems owing to widespread corruption, the control by criminal organizations of large segments of the economy, and the continuing effects of the war.
The CIS economic sanctions imposed on Abkhazia in 1996 are still formally in force although Russia announced on March 6, 2008 that it would no longer participate in them, declaring them "outdated, impeding the socio-economic development of the region, and causing unjustified hardship for the people of Abkhazia". Russia also called on other CIS members to undertake similar steps, but met with protests from Tbilisi and lack of support from the other CIS countries.
The European Union has allocated more than €20 mln. to Abkhazia since 1997 for various humanitarian projects, including the support of civil society, economic rehabilitation, help to the most vulnerable households and confidence building measures. The single largest EU's project is the repair and reconstruction of the Inguri power station.
Demographics
According to the Family Lists compiled in 1886 (published 1893 in Tbilisi) the Sukhumi District's population was 68,773, of which 30,640 were Samurzaq'anoans, 28,323 Abkhaz, 3,558 Mingrelians, 2,149 Greeks, 1,090 Armenians, 1,090 Russians and 608 Georgians (including Imeretians and Gurians). Samurzaq'ano is a present-day Gali district of Abkhazia. Most of the Samurzaq'anians must be thought to have been Mingrelians, and a minority Abkhaz.
According to the 1897 census there were 58,697 people in Abkhazia who listed Abkhaz as their mother tongue. The population of the Sukhumi district (Abkhazia) was about 100,000 at that time. Greeks, Russians and Armenians composed 3.5%, 2% and 1.5% of the district's population.
According to the 1917 agricultural census organized by the Russian Provisional Government, Georgians and Abkhaz composed 41.7% (54,760) and 30,4% (39,915) of the rural population of Abkhazia respectively. At that time Gagra and its vicinity weren't part of Abkhazia.
The following table summarises the results of the other censuses carried out in Abkhazia. The Russian, Armenian and Georgian population grew faster than Abkhaz, due to the large-scale migration enforced especially during the rule of Stalin and Lavrenty Beria, who himself was a Georgian born in Abkhazia.
| Year | Total | Georgians | Abkhaz | Russians | Armenians | Greeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1926 Census | 186,004 | 67,494 | 55,918 | 12,553 | 25,677 | 14,045 |
| 1939 Census | 311,885 | 91,967 | 56,197 | 60,201 | 49,705 | 34,621 |
| 1959 Census | 404,738 | 158,221 | 61,193 | 86,715 | 64,425 | 9,101 |
| 1970 Census | 486,959 | 199,596 | 77,276 | 92,889 | 74,850 | 13,114 |
| 1979 Census | 486,082 | 213,322 | 83,087 | 79,730 | 73,350 | 13,642 |
| 1989 Census | 525,061 | 239,872 | 93,267 | 74,913 | 76,541 | 14,664 |
| 2003 Census1 | 215,972 | 45,953 | 94,606 | 23,420 | 44,870 | 1,486 |
|
|||||||||||
History
Early history
In the 9th–6th centuries BC, the territory of modern Abkhazia became a part of the ancient Georgian kingdom of Colchis (Kolkha), which was absorbed in 63 BC into the Kingdom of Egrisi. Greek traders established ports along the Black Sea shoreline. One of those ports, Dioscurias, eventually developed into modern Sukhumi, Abkhazia's traditional capital.
The Roman Empire conquered Egrisi in the 1st century AD and ruled it until the 4th century, following which it regained a measure of independence, but remained within the Byzantine Empire's sphere of influence. Although the exact time when the population of Abkhazia was converted to Christianity is not determined, it is known that the Metropolitan of Pitius participated in the First Œcumenical Council in 325 in Nicea. Abkhazia was made an autonomous principality of the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century — a status it retained until the 9th century, when it was united with the province of Imereti and became known as the Abkhazian Kingdom. In 9th–10th centuries the Georgian kings tried to unify all the Georgian provinces and in 1001 King Bagrat III Bagrationi became the first king of the unified Georgian Kingdom.
In the 16th century, after the break-up of the united Georgian Kingdom, the area was conquered by the Ottoman Empire, during this time some Abkhazians converted to Islam. The Ottomans were pushed out by the Georgians, who established an autonomous Principality of Abkhazia (abxazetis samtavro in Georgian), ruled by the Shervashidze dynasty (aka Sharvashidze, or Chachba).
Abkhazia within the Russian Empire and Soviet Union
The expansion of the Russian Empire into the Caucasus region led to small-scale but regular conflicts between Russian colonists and the indigenous Caucasian tribes. Eventually the Caucasian War erupted, which ended with Russian conquest of the North and Western Caucasus. Various Georgian principalities were annexed to the empire between 1801 and 1864. The Russians acquired possession of Abhkazia in a piecemeal fashion between 1829 and 1842; but their power was not firmly established until 1864, when they managed to abolish the local principality which was still under Shervashidze rule. Large numbers of Muslim Abkhazians — said to have constituted as much as 60% of the Abkhazian population, although contemporary census reports were not very trustworthy — emigrated to the Ottoman Empire between 1864 and 1878 together with other Muslim population of Caucasus in the process known as Muhajirism.
Modern Abkhazian historians maintain that large areas of the region were left uninhabited, and that many Armenians, Georgians and Russians (all Christians) subsequently migrated to Abkhazia, resettling much of the vacated territory. This version of events is strongly contested by some Georgian historians who argue that Georgian tribes (Mingrelians and Svans) had populated Abkhazia since the time of the Colchis kingdom. According to these scholars, the Abkhaz are the descendants of North Caucasian tribes ( Adygey, Apsua), who migrated to Abkhazia from the north of the Caucasus Mountains and merged there with the existing Georgian population. This theory has little support though among Georgian academics.
The Russian Revolution of 1917 led to the creation of an independent Georgia (which included Abkhazia) in 1918. Georgia's Menshevik government had problems with the area through most of its existence despite a limited autonomy being granted to the region. In 1921, the Bolshevik Red Army invaded Georgia and ended its short-lived independence. Abkhazia was made a Soviet republic with the ambiguous status of Union Republic associated with the Georgian SSR. In 1931, Stalin made it an autonomous republic within Soviet Georgia. Despite its nominal autonomy, it was subjected to strong central rule from central Soviet authorities. Georgian became the official language. Purportedly, Lavrenty Beria encouraged Georgian migration to Abkhazia, and many took up the offer and resettled there. Russians also moved into Abkhazia in great numbers. Later, in the 1950s and 1960s, Vazgen I and the Armenian church encouraged and funded the migration of Armenians to Abkhazia. Currently, Armenians are the largest minority group in Abkhazia.
The repression of the Abkhaz was ended after Stalin's death and Beria's execution, and Abkhaz were given a greater role in the governance of the republic. As in most of the smaller autonomous republics, the Soviet government encouraged the development of culture and particularly of literature. Ethnic quotas were established for certain bureaucratic posts, giving the Abkhaz a degree of political power that was disproportionate to their minority status in the republic. This was interpreted by some as a "divide and rule" policy whereby local elites were given a share in power in exchange for support for the Soviet regime. In Abkhazia as elsewhere, it led to other ethnic groups - in this case, the Georgians - resenting what they saw as unfair discrimination, thereby stoking ethnic discord in the republic.
The Abkhazian War
As the Soviet Union began to disintegrate at the end of the 1980s, ethnic tensions grew between the Abkhaz and Georgians over Georgia's moves towards independence. Many Abkhaz opposed this, fearing that an independent Georgia would lead to the elimination of their autonomy, and argued instead for the establishment of Abkhazia as a separate Soviet republic in its own right. The dispute turned violent on July 16, 1989 in Sukhumi. Sixteen Georgians are said to have been killed and another 137 injured when they tried to enrol in a Georgian University instead of an Abkhaz one. After several days of violence, Soviet troops restored order in the city and blamed rival nationalist paramilitaries for provoking confrontations.
The Republic of Georgia boycotted the March 17, 1991 all-Union referendum on the renewal of the Soviet Union called by Mikhail Gorbachev - but 52.3% of the Abkhazia's population (virtually all the ethnic non-Georgians) took part in the referendum and voted by an overwhelming majority (98.6%) to preserve the Union. Most ethnic non-Georgians later boycotted a March 31 referendum on Georgia’s independence, which was supported by a huge majority of Georgia's population. Within weeks, Georgia declared independence on 9 April 1991, under former Soviet dissident Zviad Gamsakhurdia. Under Gamsakhurdia, the situation was relatively calm in Abkhazia and a power-sharing agreement was soon reached between the Abkhaz and Georgian factions, granting to the Abkhaz a certain overrepresentation in the local legislature.
Gamsakhurdia's rule was soon challenged by the armed opposition groups which, under the command of Tengiz Kitovani, forced him to flee the country in a military coup in January 1992. Former Soviet foreign minister and architect of the disintegration of the USSR Eduard Shevardnadze replaced Gamsakhurdia as president, inheriting a government dominated by hardline Georgian nationalists. He was not an ethnic nationalist but did little to avoid being seen as supporting his administration's dominant figures and the leaders of the coup that swept him to power.
On 21 February 1992, Georgia's ruling Military Council announced that it was abolishing the Soviet-era constitution and restoring the 1921 Constitution of the Democratic Republic of Georgia. Many Abkhaz interpreted this as an abolition of their autonomous status although the constitution did provide a provision for the region's autonomy. On 23 July 1992, the Abkhaz faction in the republic's Supreme Council declared effective independence from Georgia, although the session was boycotted by ethnic Georgian deputies and the gesture went unrecognised by any other country. The Abkhaz leadership launched a campaign of ousting Georgian officials from their offices, a process which which was accompanied by violence. In the meantime, the Abkhaz leader Ardzinba intensified his ties with the hardliner Russian politicians and military elite and declared he was ready for a war with Georgia.
In August 1992, the Georgian government accused Gamsakhurdia's supporters of kidnapping Georgia's interior minister and holding him captive in Abkhazia. The Georgian government dispatched 3,000 troops to the region, ostensibly to restore order. The Abkhaz were relatively unarmed at this time and the Georgian troops were able to march into Sukhumi with relatively little resistance and subsequently engaged in ethnically based pillage and looting. The Abkhaz units were forced to retreat to Gudauta and Tkvarcheli.
The Abkhaz military defeat was met with a hostile response by the self-styled Confederation of Mountain Peoples of the Caucasus, an umbrella group uniting a number of pro-Russian movements in the North Caucasus, including Circassians, Abazas, Chechens, Cossacks, Ossetians and hundreds of volunteer paramilitaries from Russia, including the then little-known Shamil Basayev, later a leader of the anti-Moscow Chechen secession, sided with the Abkhaz separatists to fight the Georgian government. Regular Russian forces also reportedly sided with the secessionsts. In September, the Abkhaz and Russian paramilitaries mounted a major offensive against Gagra after breaking a cease-fire, which drove the Georgian forces out of large swathes of the republic. Shevardnadze's government accused Russia of giving covert military support to the rebels with the aim of "detaching from Georgia its native territory and the Georgia-Russian frontier land". The year 1992 ended with the rebels in control of much of Abkhazia northwest of Sukhumi. The conflict remained in stalemate until July 1993, when Abkhaz separatist militias launched an abortive attack on Georgian-held Sukhumi. They surrounded and heavily shelled the capital, where Shevardnadze was trapped. The warring sides declared a truce at the end of July, but it collapsed in mid-September 1993 after a renewed Abkhaz attack. After ten days of heavy fighting, Sukhumi fell on 27 September 1993. Shevardnadze narrowly escaped death, after vowing to stay in the city no matter what. He was forced to flee when separatist snipers fired on the hotel where he was staying. Abkhaz, North Caucasian militants and their allies committed numerous atrocities against the city's remaining ethnic Georgians, in what has been dubbed the Sukhumi Massacre. The mass killings and destruction continued for two weeks, leaving thousands dead and missing.
The Abkhaz forces quickly overran the rest of Abkhazia as the Georgian government faced a second threat: an uprising by the supporters of the deposed Zviad Gamsakhurdia in the region of Mingrelia (Samegrelo). In the chaotic aftermath of defeat almost all ethnic Georgians fled the region, escaping an ethnic cleansing initiated by the victors. Many thousands died — it is estimated that between 10,000-30,000 ethnic Georgians and 3,000 ethnic Abkhaz may have perished — and some 250,000 people (mostly Georgians) were forced into exile.
During the war, gross human rights violations were reported on the both sides (see Human Rights Watch report). In the first phase of the war, Georgian troops have been accused of looting while Georgia blames the Abkhaz forces and their allies for an intentional ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia, which has also been recognized by the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) Summits in Budapest (1994), Lisbon (1996) and Istanbul (1999).
Politics

Much of the politics in Abkhazia is dominated by the territorial dispute with Georgia, from which the territory seceded, and by the fight over the presidency in 2004/2005.
On 3 October 2004 presidential elections were held in Abkhazia. In the elections, Russia evidently supported Raul Khajimba, the prime minister backed by the ailing outgoing separatist President Vladislav Ardzinba. Posters of Russia's President Vladimir Putin together with Khajimba, who like Putin had worked as a KGB official, were everywhere in Sukhumi. Deputies of Russia's parliament and Russian singers, led by Joseph Kobzon, a deputy and a popular singer, came to Abkhazia campaigning for Khajimba.
However Raul Khajimba lost the elections to Sergey Bagapsh. The tense situation in the republic led to the cancellation of the election results by the Supreme Court. After that a deal was struck between former rivals to run jointly — Bagapsh as a presidential candidate and Khajimba as a vice presidential candidate. They received more than 90% of the votes in the new election.
The President appoints districts' heads from those elected to the districts assemblies. There are elected village assemblies whose heads are appointed by the districts heads.
The People's Assembly, consisting of 35 elected members, is vested with legislative powers. The last parliamentary elections were held on March 4, 2007. The ethnicities other than Abkhaz (Armenians, Russians and Georgians) are believed to be under-represented in the Assembly as the number of the parliamentarians of these ethnicities is less than their share in the republic population.
About 250,000 ethnic Georgian residents of Abkhazia are restricted from settling in the region by the Abkhazian separatist regime and cannot participate in the elections.
Government of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia
The Government of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia, formerly known as The Council of Ministers of the Abkhazian Autonomous Republic, is the only government that Georgia recognizes as the legal government of Abkhazia. After the Kodori crisis of 2006, the Government of the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia, along with its ministers, relocated to the north-eastern part of Abkhazia (known as Upper Abkhazia) in Chkhalta.
The Council of Ministers of the autonomous republic was created during the Soviet period which included the Presidium where representatives (elected) from all regions in Abkhazia governed the affairs of the republic. The members of the Cabinet of Ministers and the Presidium included ethnic Georgians, Abkhaz and Armenians.
Zhiuli Shartava was elected as the Chairman of the Council of Ministers just before the outbreak of the war. When the hostilities reached their climax in 1992, the separatist wing of the government left the Presidium and moved to Gudauta. From Gudauta they started to arm militia groups (allegedly supplied by the Russian military base in Gudauta) which were used during the conflict.
The Council of Ministers remaining in Sukhumi still maintained its ethnic Abkhaz representatives, who rejected the separatist call for secession. Two of them, leading Abkhaz politician Raul Eshba and Sumbat Saakian, a representative of the ethnic Armenian Diaspora, refused to leave Sukhumi and stayed along with Zhiuli Shartava, Guram Gabiskiria and other members of the government in Sukhumi until the tragic events of September 27th 1993, when Shartava, Eshba, Gabiskiria, Saakian and other members of the government were tortured and killed by the separatists and their allies (see Sukhumi massacre). The remaining survivors of the government fled to the capital Tbilisi where they organized the headquarters of the Abkhaz government in exile headed by Tamaz Nadareishvili (great grandson of Abkhaz Prince Shervashidze). In 1998, Georgians in the Gali district (populated mainly by ethnic Georgians) of Abkhazia launched partisan activities against the de facto authorities in Sukhumi. The Abkhaz government in exile allegedly supported the rebel movement known as The White Legion. However, as a result of this insurrection, the Abkhaz separatist authorities launched a full scale attack on the Gali region, killing and expelling its ethnic Georgian inhabitants. In 2004, Nadareishvili died leaving the government in a disorganized state. After the Rose Revolution and Kodori events of 2006, the de jure Abkhaz government was revived and reorganized. Malkhaz Akishbaia, a Western-educated Abkhaz politician was elected in April 2006 and is the current head of the de jure Government of Abkhazia. Akishbaia appointed ethnic Abkhaz ministers Temur Mzhavia and Ada Marshania to key positions and included former members of Council of Ministers in his government. The government moved to Upper Abkhazia (within the administrative borders of the autonomous republic) with its headquarters in Chkhalta. On September 27, 2006 President Mikheil Saakashvili, Nino Burjanadze, Catholicos-Patriarch of All Georgia Ilia II and others members of the central government visited Kodori Valley and officially changed the name and designated the area as "Upper Abkhazia".
The NGO the International Crisis Group has urged Georgia to lower the Abkhaz government in exile’s profile in the Kodori Gorge significantly and refrain from holding alternative elections for local government or parliamentary representatives in Abkhazia.
International involvement
The UN has played various roles during the conflict and peace process: a military role through its observer mission ( UNOMIG); dual diplomatic roles through the Security Council and the appointment of a Special Envoy, succeeded by a Special Representative to the Secretary-General; a humanitarian role ( UNHCR and UNOCHA); a development role ( UNDP); a human rights role ( UNCHR); and a low-key capacity and confidence-building role ( UNV). The UN’s position has been that there will be no forcible change in international borders. Any settlement must be freely negotiated and based on autonomy for Abkhazia legitimized by referendum under international observation once the multi-ethnic population has returned. According to Western interpretations the intervention did not contravene international law since Georgia, as a sovereign state, had the right to secure order on its territory and protect its territorial integrity.
OSCE has increasingly engaged in dialogue with officials and civil society representatives in Abkhazia, especially from NGOs and the media, regarding human dimension standards and is considering a presence in Gali. OSCE expressed concern and condemnation over ethnic cleansing of Georgians in Abkhazia during the 1994 Budapest Summit Decision and later at the Lisbon Summit Declaration in 1996.
The USA rejects the unilateral secession of Abkhazia and urges its integration into Georgia as an autonomous unit. In 1998 the USA announced its readiness to allocate up to $15 million for rehabilitation of infrastructure in the Gali region if substantial progress is made in the peace process. USAID has already funded some humanitarian initiatives for Abkhazia. The USA has in recent years significantly increased its military support to the Georgian armed forces but has stated that it would not condone any moves towards peace enforcement in Abkhazia.
On August 22, 2006, Senator Richard Lugar, then visiting Georgia's capital Tbilisi, joined the Georgian politicians in criticism of the Russian peacekeeping mission, stating that "the U.S. administration supports the Georgian government’s insistence on the withdrawal of Russian peacekeepers from the conflict zones in Abkhazia and the Tskhinvali district."
On October 5, 2006, Javier Solana, the High Representative for the Common Foreign and Security Policy of the European Union, ruled out the possibility of replacing the Russian peacekeepers with the EU force." On October 10, 2006, EU South Caucasus envoy Peter Semneby noted that "Russia's actions in the Georgia spy row have damaged its credibility as a neutral peacekeeper in the EU's Black Sea neighbourhood."
On October 13, 2006, the UN Security Council unanimously adopted a resolution, based on a Group of Friends of the Secretary-General draft, extending the UNOMIG mission until April 15, 2007. Acknowledging that the "new and tense situation" resulted, at least in part, from the Georgian special forces operation in the upper Kodori Valley, urged the country to ensure that no troops unauthorized by the Moscow ceasefire agreement were present in that area. It urged the leadership of the Abkhaz side to address seriously the need for a dignified, secure return of refugees and internally displaced persons and to reassure the local population in the Gali district that their residency rights and identity will be respected. The Georgian side is "once again urged to address seriously legitimate Abkhaz security concerns, to avoid steps which could be seen as threatening and to refrain from militant rhetoric and provocative actions, especially in upper Kodori Valley". Calling on both parties to follow up on dialogue initiatives, it further urged them to comply fully with all previous agreements regarding non-violence and confidence-building, in particular those concerning the separation of forces. Regarding the disputed role of the peacekeepers from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the Council stressed the importance of close, effective cooperation between UNOMIG and that force and looked to all sides to continue to extend the necessary cooperation to them. At the same time, the document reaffirmed the "commitment of all Member States to the sovereignty, independence and territorial integrity of Georgia within its internationally recognized borders."
The HALO Trust, an international non-profit organisation that specialises in the removal of the debris of war, has been active in Abkhazia since 1999 and has completed the removal of land-mines in Sukhumi and Gali districts. It plans to finish its operations in 2007/2008 and to declare Abkhazia a "mine impact free" territory.
Religion
The population (including all ethnic groups) of Abkhazia are majority Orthodox Christians (approx. 75%) and Sunni Muslims (approx. 10%). Most of the ethnic Armenians living in Abkhazia belong to the Armenian Apostolic Church. However, most of the people who declare themselves Christian or Muslim do not attend religious services. There is also a very small number of Jews, Jehovah's Witnesses and the followers of new religions. The Jehovah's Witnesses organization has officially been banned since 1995, though the decree is not currently enforced.
According to the constitutions of Georgia, Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia and de facto Republic of Abkhazia the adherents of all religions (as well as atheists) have equal rights before the law.
Abkhazia is recognized by the Eastern Orthodox world as a canonical territory of the Georgian Orthodox Church, which has been unable to operate in the region since the War in Abkhazia. Currently, the religious affairs of local Orthodox Christian community is run by the self-imposed "Eparchy of Abkhazia" under significant influence of the Russian Orthodox Church.