Image:Hafnium lump thin film effects.jpg
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Size of this preview: 564 × 480 pixels
Full resolution (1,824 × 1,551 pixels, file size: 434 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Summary
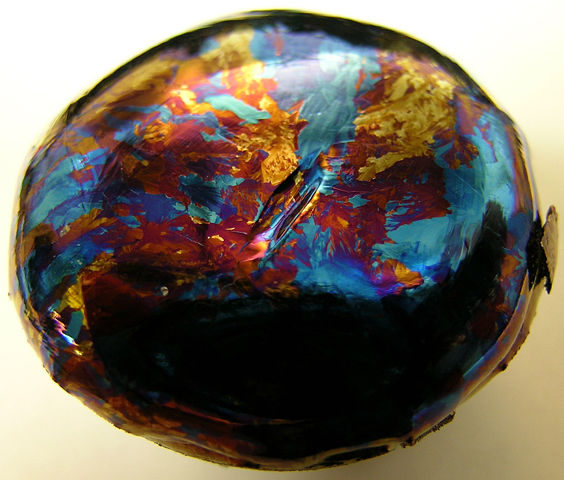
Upper side of a lump of highly pure hafnium used for evaporating as HfO2 onto glass along with silica to form multi layer dielectric optics. The vibrant colors seen here are a result of the lump being exposed to air (oxygen) while it was still hot after being used in an evaporating chamber where it is melted and vaporized using high intensity electron beams. The oxidized upper surface of the lump formed layers of differing thickness which interact with ambient light via bragg diffraction to form rich saturated colors in reflection.
Licensing
 |
I, the creator of this work, hereby grant the permission to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. Subject to disclaimers. |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 04:13, 24 December 2006 | 1,824×1,551 (434 KB) | Deglr6328 ( Talk | contribs) | (Upper side of a lump of highly pure hafnium used for evaporating as HfO<sub>2</sub> onto glass along with silica to form multi layer dielectric optics. The vibrant colors seen here are a result of the lump being exposed to air (oxygen) while it was still ) |
See the setup instructions for more information.
File links
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Camera manufacturer | NIKON |
|---|---|
| Camera model | E5400 |
| Exposure time | 10/39 sec (0.25641025641) |
| F-number | f/2.8 |
| Date and time of data generation | 03:51, 10 December 2006 |
| Lens focal length | 5.8 mm |
| Orientation | Normal |
| Horizontal resolution | 300 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 300 dpi |
| Software used | E5400v1.3 |
| File change date and time | 03:51, 10 December 2006 |
| Y and C positioning | 2 |
| Exposure Program | Normal program |
| ISO speed rating | 59 |
| Exif version | 2.2 |
| Date and time of digitizing | 03:51, 10 December 2006 |
| Image compression mode | 4 |
| Exposure bias | 0 |
| Maximum land aperture | 3 |
| Metering mode | Pattern |
| Light source | Unknown |
| Flash | 16 |
| Colour space | sRGB |
| Custom image processing | Normal process |
| Exposure mode | Auto exposure |
| White balance | Auto white balance |
| Digital zoom ratio | 0 |
| Focal length in 35 mm film | 28 |
| Scene capture type | Standard |
| Contrast | Normal |
| Saturation | Normal |
| Sharpness | Normal |
| Subject distance range | Unknown |