Isles of Scilly
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Geography of Great Britain
 An aerial photo of the islands |
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
 Location in relation to Cornwall |
|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean, 45 km (28 mi) off the coast of Great Britain |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: |
| Total islands | 5 inhabited, 140 others |
| Major islands | St Mary's, Tresco, St Martins, Bryher, St Agnes |
| Area | 16.33 km² (6.3 sq mi) ( ranked 351st) |
| Highest point | () |
| Administration | |
| Status | Sui generis, Unitary |
| Largest city | Hugh Town (1,068) |
| Leadership | Cllr. Mrs. Christine Savill |
| Executive | Philip Hygate B.A., F.R.S.A. |
| MP | Andrew George |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 2,100 ( ranked 354th) (as of 2006) |
| Density | 129 / km²/km² |
| Ethnic groups | 99.6% Caucasian |
The Isles of Scilly ( Cornish: Ynysek Syllan) form an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Great Britain. Traditionally administered as part of the county of Cornwall, the islands now have their own Council of the Isles of Scilly. They are also designated the Isles of Scilly Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
The correct name for the islands is the Isles of Scilly, or simply Scilly; the people of Scilly consider the terms "Scillies" and "Scilly Isles" to be incorrect. The adjective "Scillonian" is sometimes used for people or things related to the archipelago.
Geography
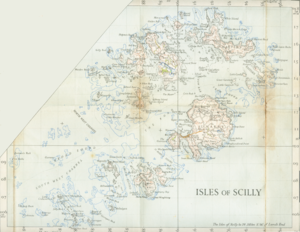
The Isles of Scilly, the most westerly part of England, form an archipelago of six inhabited islands and numerous other small rocky islets (around 140 in total) lying 45 km (28 miles) off Land's End. The table provides an overview of the most important islands:
| Island | Population ( Census 2001) |
Area km² |
Main settlement |
|---|---|---|---|
| St Mary's | 1,666 | 6.29 | Hugh Town |
| Tresco | 180 | 2.97 | New Grimsby |
| St Martin's (with White Island) | 142 | 2.37 | Higher Town |
| St Agnes | 70 | 1.48 | Saint Agnes |
| Gugh | 3 | ||
| Bryher (with Gweal) | 92 | 1.32 | Bryher |
| Samson | -(1) | 0.38 | |
| Annet | - | 0.21 | |
| St. Helen's | - | 0.20 | |
| Teän | - | 0.16 | |
| Great Ganilly | - | 0.13 | |
| remaining 45 islets | - | 0.50 | |
| Isles of Scilly | 2,153 | 16.03 | Hugh Town |
(1) inhabited until 1855
The islands' position produces a place of great contrast—the ameliorating effect of the sea means they rarely have frost or snow, which allows local farmers to grow flowers well ahead of those on the island of Britain. The largest agricultural product is cut flowers, mostly daffodils. Exposure to Atlantic winds means that spectacular winter gales lash the islands from time to time.
This is reflected in the landscape, most clearly seen on Tresco where the lush sub-tropical Abbey Gardens on the sheltered southern end of the island contrast with the low heather and bare rock sculpted by the wind on the exposed northern end.
As part of a 2002 marketing campaign, the plant conservation charity Plantlife chose Thrift (Armeria maritima) as the "county flower" of the islands.
History
Scilly has been inhabited since the Stone Age and its history has been one of subsistence living until the 20th century with people living off the land and the sea. Farming and fishing continue today, but the main industry now is tourism.
The islands may correspond to the Cassiterides (Tin Isles) visited by the Phoenicians and mentioned by the Greeks. However, the archipelago itself does not contain much tin - it may be that they were used as a staging post from the mainland.
It is likely that until relatively recently the Isles were much larger with many of them joined into one island and that the land has subsided. Evidence for this includes:
- A description in Roman times describes Scilly as "Scillonia insula" in the singular, as if there was an island much bigger than any of the others.
- Remains of a prehistoric farm have been found on Nornour, which is now a small rocky skerry far too small for farming.
- At certain low tides the sea becomes shallow enough for people to walk between some of the islands. This is possibly one of the sources for stories of drowned lands, e.g., Lyonesse.
- Ancient field walls are visible below the high tide line off some of the islands (e.g. Samson).
- Some of the Cornish language placenames also appear to reflect past shorelines, and former land areas.
Offshore, midway between Land's End and the Isles of Scilly, is the supposed location of the mythical lost land of Lyonesse, referred to in Arthurian literature. This may be a folk memory of inundated lands, but this legend is also common amongst the Brythonic peoples; the legend of " Ys" is a parallel and cognate legend in Brittany.
Norse and Norman period

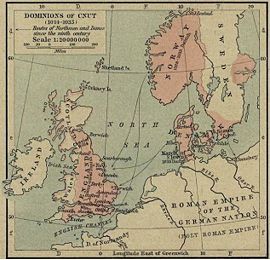
It is generally considered that Cornwall, and possibly the Isles of Scilly came under the dominion of the English Crown in the time of Athelstan's rule, i.e. 924-939, if the English crown as such can be said to have actually existed at that time.
During the latter part of the pre-Norman period, the eastern seaboard of modern-day England came increasingly under the sway of the Norse. The Isles of Scilly, called Syllingar by the Norse, themselves came under Viking attack, as it is recorded in the Orkneyinga saga - Swein Asleifsson "went south, under Ireland, and seized a barge belonging to some monks in Syllingar and plundered it." (Chap LXXIII)
- "...the three chiefs - Swein , Þorbjörn and Eirik - went out on a plundering expedition. They went first to the Suðreyar [Hebrides], and all along the west
to the Syllingar, where they gained a great victory in Maríuhöfn on Columba's-mass [9th June], and took much booty. Then they returned to the Orkneys."</quote>
"Maríuhöfn", literally means "Mary's Harbour/Haven". The name doesn't make it clear whether it referred to a harbour on a larger island than today's St Mary's, or a whole island.
In 995 Olaf Tryggvason would become King Olaf I of Norway. Born c. 960, Olaf had raided various European cities and fought in several wars. In 986 however, he (supposedly) met a Christian seer on the Isles of Scilly. In Snorre Sturlason's Royal Sagas of Norway, it is stated that this seer told him:
- Thou wilt become a renowned king, and do celebrated deeds. Many men wilt thou bring to faith and baptism, and both to thy own and others' good; and that thou mayst have no doubt of the truth of this answer, listen to these tokens. When thou comest to thy ships many of thy people will conspire against thee, and then a battle will follow in which many of thy men will fall, and thou wilt be wounded almost to death, and carried upon a shield to thy ship; yet after seven days thou shalt be well of thy wounds, and immediately thou shalt let thyself be baptized.
The legend continues that, as the seer foretold, Olaf was attacked by a group of mutineers upon returning to his ships. As soon as he had recovered from his wounds, he let himself be baptized. He then stopped raiding Christian cities and lived in England and Ireland. In 995 he used an opportunity to return to Norway. When he arrived, the Haakon Jarl was already facing a revolt. Olaf Tryggvason convinced the rebels to accept him as their king, and Haakon Jarl killed by his own slave, while he was hiding from the rebels in a pig sty.)
Eventually England became ruled by Norse monarchs, and the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms fell one by one, with Wessex being conquered in 1013 by King Sweyn Forkbeard. Notably, while Sweyn's realms, which included Denmark and Norway in the north, and modern-day English areas such as Mercia (an Anglian kingdom of the current Midlands), much of which, along with northern England, fell under the " Danelaw". But while Sweyn ruled Wessex, along with his other realms, from 1013 onwards, followed by his son Canute the Great, the Isles of Scilly were not part of his realm of Wessex.
With the Norman Conquest, the Isles of Scilly came more under centralised control. About twenty years later, the Domesday survey was conducted. The islands would have formed part of the " Exeter Domesday" circuit, which included Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, and Wiltshire.
Middle Ages and early modern period
At the turn of the 14th century, the Abbot and convent of Tavistock Abbey petitioned the king saying that
- "state that they hold certain isles in the sea between Cornwall and Ireland, of which the largest is called Scilly, to which ships come passing between France, Normandy, Spain, Bayonne, Gascony, Scotland, Ireland, Wales and Cornwall: and, because they feel that in the event of a war breaking out between the kings of England and France, or between any of the other places mentioned, they would not have enough power to do justice to these sailors, they ask that they might exchange these islands for lands in Devon, saving the churches on the islands appropriated to them."
William le Poer, coroner of Scilly is recorded in 1305, about being worried about the extent of wrecking in the islands, and sent a petition to the King. The names provide a wide variety of origins, e.g. Robert and Henry Sage (English), Richard de Tregenestre (Cornish), Ace de Veldre (French), Davy Gogch (possibly Welsh, or Cornish), and Adam le Fuiz Yaldicz (?Spanish)
In 1375, Boreman, with 28 mariners, was captured in the Isles of Scilly in a barge of Normandy by Fulbroke, Borde and others and brought to Bristol as prisoners.
It is not known at exactly what time the islands' inhabitants stopped speaking Cornish, but it seems to have gone into decline during the Middle Ages, and lost the language before parts of Penwith. The islands thus appeared to have lost the old Celtic language before parts of the mainland, in contrast to the situation of Irish or Scottish Gaelic.
During the English Civil War, the Parliamentarians captured the isles, only to see its garrison mutiny and return them to the Royalists. By 1651, the Royalist governor, Sir John Grenville, was using the islands as a base of privateering raids on Commonwealth and Dutch shipping. It was during this period that the Three Hundred and Thirty Five Years' War started between the isles and the Netherlands. In June 1651, Admiral Robert Blake captured the isles for the Parliamentarians. Blake's initial attack, on Old Grimsby, failed, but the next attacks, succeeded in taking Tresco and Bryher. Blake set up a battery on Tresco to fire on St. Mary's, but one of the guns exploded, killing its crew and injuring Blake himself. Still, a second battery proved more successful. Consequently, Grenville and Blake negotiated terms that permitted the Royalists to surrender honorably. The Parliamentary forces then set to fortifying the islands. They built Cromwell's Castle - a gun platform on the west side of Tresco - using materials scavenged from an earlier gun platform further up the hill. Although this poorly sited earlier platform dated back to the 1550s, it is now referred to King Charles's Castle.
The islands appear to have been depredated frequently by Barbary pirates.
Modern period
Scilly is famous for its danger to shipping and its many shipwrecks. The wreck of Sir Cloudesley Shovell's ship HMS Association and three others of his fleet in 1707 off the Isles of Scilly due to inaccuracies in navigation led to the establishment of the Board of Longitude and consequently the development of the method of lunar distances, and to the invention of the marine chronometer by John Harrison, the first reliable methods of determining longitude at sea.
The sea has always played a huge part in Scillonian history but it was in the 19th century that Scilly had its maritime heyday. Beaches which are now enjoyed by sunbathers were then factories for shipbuilding; the harbours now full of pleasure boats were once packed with local and visiting fishing and trading boats.
In 1834, Augustus Smith acquired the lease on the Isles of Scilly from the Duchy of Cornwall for £20,000, and set about changing the islanders' way of life, expelling those who could not find a job locally and evicting some of the inhabitants of smaller islands, in a manner similar to that practiced in the Scottish clearances. In 1855, he expelled the ten inhabitants of Samson, in order to turn the island into a deer park. (The deer did not like the habitat, and escaped.)
Smith created the quasi-aristocratic title Lord Proprietor for himself, and, many of his actions were unpopular. However, it can be said that not all his actions were detrimental to the inhabitants, for example, besides building a new quay at Hugh Town on St. Mary's, he sowed gorse and trees to provide shelter for the agricultural land. He built schools on the well-inhabited islands. These were the first compulsory schools in the whole of Britain. It cost one penny a time but if you missed school then it was 2d.
The archipelago became fairly popular in the 20th century as a holiday and holiday home location. For example, former Prime Minister Harold Wilson regularly holidayed on the Isles and eventually bought a cottage there as a holiday home. He is buried on St Mary's. His widow Mary Wilson is still a frequent visitor.
Government
Local government
Historically, the Isles of Scilly were administered as one of the hundreds of Cornwall, although the Cornwall quarter sessions had limited jurisdiction there. The archipelago is part of the Duchy of Cornwall, the Duke being the heir to the British throne, and he is allowed special rights and privileges in the islands.
The Local Government Act 1888 allowed the Local Government Board to establish in the Isles of Scilly "councils and other local authorities separate from those of the county of Cornwall"... "for the application to the islands of any act touching local government." Accordingly, in 1890 the Isles of Scilly Rural District Council (the RDC) was formed as a sui generis unitary authority, outside the administrative county of Cornwall. Cornwall County Council provided some services to the Isles, for which the RDC made financial contributions. Section 265 of the Local Government Act of 1972 allowed for the continued existence of the RDC, but renamed as the Council of the Isles of Scilly.
This unusual status also means that much administrative law (for example relating to the functions of local authorities, the health service and other public bodies) that applies in the rest of England applies in modified form in the islands.
With a total population of just over 2,000, the council represents fewer inhabitants than many U.K parish councils, and is by far the smallest unitary council within the UK. In 2005, there were 21 elected councillors (all independent), 13 elected by St Mary's residents and two each, elected by residents of Bryher, St Martins, St Agnes and Tresco. There are some 164 staff employed by the council. These numbers are significant in that almost 10 per cent of the population is directly linked to the council as either an employee or councillor.
For judicial, shrievalty and lieutenancy purposes the Isles of Scilly are "deemed to form part of the county of Cornwall".
National government
The phrase "England and Cornwall" (or the Latin equivalent Anglia et Cornubia) remained in use after the Norman Conquest. Before the Tudor period, laws were typically designated as taking effect in Anglia et Cornubia. A similar situation exists today with the Isles of Scilly within Cornwall (i.e Cornwall and the Isles of Scilly). Both the relationship of Cornwall to the Isles of Scilly, and the constitutional status of Cornwall are a matter of some debate.
Politically, the islands are part of the United Kingdom. They are represented in the United Kingdom Parliament as part of the St Ives constituency, currently held by Andrew George of the Liberal Democrats.
As part of the United Kingdom, the islands are part of the European Union and are represented in the European Parliament as part of the multi-member South West England constituency. The Isles of Scilly are not the most remote part of this constituency, as it also includes the United Kingdom dependent territory of Gibraltar.
Flags
There are primarily two flags used to represent Scilly:
- The flag of the Council of the Isles of Scilly, which incorporates their logo.
- The unofficial Scillonian Cross, voted for by readers of Scilly News
An adapted version of the old Board of Ordnance flag has also been used, after it was left behind when munitions were removed from the isles. The Cornish Ensign has also been used.
Education
Education is available on the islands up to age 16. There is one school, the Five Islands School, which provides primary schooling at sites on St Agnes, St Mary's, St Martin's and Tresco, and secondary schooling at a site on St Mary's. Secondary students from outside St Mary's live at a hostel during the week. In 2004, 93% of pupils (26 out of 28) achieved 5 or more GCSEs at grade C and above, compared to the English average of 53.7%. Sixteen to eighteen year olds are entitled to a free sixth form place at a state school or sixth form college on the mainland, and are provided with free flights and a grant towards accommodation. Post eighteen, suitably qualified students attend universities and colleges on the mainland.
Subdivisions
The Isles of Scilly are subdivided into four wards that have no administrative function, but only serve statistical purposes :
- St. Agnes
- St. Martin's
- St. Mary's
- Tresco
The list of parishes, also without any administrative function since 1929, numbers five :
- Bryher
- St. Agnes
- St. Martin's
- St. Mary's
- Tresco
Economy
Historical context
Since the mid-eighteenth century the Scillionian economy has relied on trade with the mainland and beyond as a means of sustaining its population. Over the years the nature of this trade has varied, due to wider economic and political factors that have seen the rise and fall of industries such as kelp harvesting, pilotage, smuggling, fishing, shipbuilding and, latterly, flower farming. In a study of the Scillionian economy by Neate in 1987, it was found that many farms on the islands were struggling to remain profitable due to increasing costs and strong competition from overseas producers resulting in a diversification into tourism. Recent statistics suggest that agriculture on the islands now represent less than 2 percent of all employment.
Tourism
Today, tourism is estimated to account for 85 per cent of the island's income. The islands have been efficient in attracting this investment due to its unique environment, favourable summer climate, relaxed culture, efficient co-ordination of tourism providers and good transport links by sea and air to the mainland, uncommon in scale to similar sized island communities. The majority of visitors stay on St Mary's, which has a concentration of holiday accommodation and other amenities. Of the other inhabited islands, Tresco is run as a timeshare resort, and is consequently the most obviously tourist-orientated. Bryher and St Martin's are more unspoilt, although each has a hotel and other accommodation. St Agnes has no hotel and is the least developed of the islands.
However the level of dependency on tourism is high, even by the standards of other island communities. “The concentration [on] a small number of sectors is typical of most similarly sized UK island communities. However, it is the degree of concentration, which is distinctive along with the overall importance of tourism within the economy as a whole and the very limited manufacturing base that stands out.”
Due to its scale, tourism stands to justify the existence of many other island activities, for example, transport links to the mainland which could not be maintained with reduced visitor numbers. Therefore the implications of tourism are far ranging, as they essentially affect the sustainability of the whole community.
Tourism is also a highly seasonal industry due to its reliance on outdoor recreation, and the low level of tourist activity in winter causes a near shutdown of the islands during that season. However, the tourist season benefits from an extended period of business in October when many birdwatchers (or birders) arrive. Because of its position, Scilly is the first landing for many migrant birds, including extreme rarities from North America and Siberia.
Employment
The predominance of tourism means that "tourism is by far the main sector throughout each of the individual islands, in terms of employment… [and] this is much greater than other remote and rural areas in the United Kingdom”. Tourism accounts for approximately 63 per cent of all employment.
Businesses dependent on tourism, with the exception of a few hotels, tend to be small enterprises typically employing fewer than 4 people and many of these are family run suggesting an entrepreneurial culture amongst the local population. However, much of the work generated by this, with the exception of management, is low skilled and thus poorly paid, especially for those involved in cleaning, catering and retail.
Because of the seasonality of tourism, many jobs on the islands are seasonal and part time as work cannot be guaranteed throughout the year. Some islanders take up other temporary jobs ‘out of season’ to compensate for this. Due to a lack of local casual labour at peak holiday times, many of the larger employers accommodate guest workers who come to the islands for the summer to have a ‘working holiday’.
Transport
The islands are linked to the mainland by both air and sea services, and rely on boat services for inter-island connections. St. Mary's is the only island with a significant road network.
By air, the islands are served by St. Mary's Airport on the main island of St. Mary's and by Tresco Heliport on the island of Tresco. The following air services currently operate:
- Helicopter services, operated by British International Helicopters, from Penzance Heliport to St. Mary's Airport and Tresco Heliport.
- Fixed-wing aircraft services, operated by Isles of Scilly Skybus, from various UK airports ( Land's End, Newquay, Exeter, Bristol and Southampton) to St Mary's Airport.
By sea, the Isles of Scilly Steamship Company provides a passenger and cargo service from Penzance to St Mary's: Scillonian III passenger ferry and Gry Maritha cargo vessel. The other islands are linked to St. Mary's by a network of inter-island launches.
Real estate
The freehold of the islands is the property of the British Crown (except for Hugh Town on St Mary's, which was sold to the inhabitants in 1949). The crown estate on the islands is administered by the Duchy of Cornwall. The duchy also holds 3,921 acres (16 km²) as duchy property, part of the duchy's landholding.
Housing availability is a contentious yet critical issue for the Isles of Scilly, especially as it affects the feasibility of residency on the islands. Few properties are privately owned, with many units being let by the Duchy of Cornwall, the Council, and a few by housing associations. The management of these subsequently impacts the possibility of residency on the islands.
Housing demand outstrips supply, a problem compounded by restrictions on further development designed to protect the islands' unique environment and prevent the infrastructural carrying capacity from being exceeded. This has pushed up the prices fetched for the few private properties that become available, but significantly for the majority of the island's population, this has also impacted the rental sector where rates have likewise drastically increased.
High housing costs pose significant problems of affordability for the local population, especially as local incomes (in Cornwall) are only 70% of the national average, whilst house prices are almost £5,000 more than the national average. This in turn affects the retention of ‘key workers’ and the younger generation, which has a consequent impact upon the viability of the school(s) and other essential community services.
The access to housing provokes strong local politics. It is often assumed that tourism is to blame for this, attracting incomers to the area who can afford to out-price locals for available housing. Many buildings are used for tourist accommodation which reduces the number available for local residency. Second homes are also thought to account for a significant proportion of the housing stock, leaving many buildings empty for much of the year.
Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
In 1975, the islands were designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The designation covers the entire archipelago, including the uninhabited islands and rocks, and is the smallest such area in the UK. The islands of Annet and Samson have large terneries and the islands are well populated by seals. The Isles of Scilly are the only British haunt of the Lesser White-toothed Shrew (Crocidura suaveolens).
The islands are famous amongst birdwatchers, especially twitchers for their almost magnetic ability to attract rare birds from all corners of the globe. The peak time of year for this is generally in October when it is not unusual for several of the rarest birds in Europe to share this archipelago. One reason for the success of these islands in producing rarities is the extensive coverage these islands get from birdwatchers, but island archipelagos are favoured by rare birds which like to make landfall and eat before continuing their journeys and often arrive on far flung islands first.
Culture
People
The vast majority of the population are either Cornish or English, the latter mainly from the Home Counties, and the ethnic makeup of the islands is almost exclusively white European. As with other parts of the UK, a large number of Central and Eastern Europeans, particularly Poles have been brought in to do low paid labour in the early 21st century.
Whilst there is little evidence to substantiate the claim, it is sometimes rather tenuously suggested, that the early inhabitants of the islands may have had a genetic link to the "Ancient British" who inhabited the islands long before the arrival of the Celts or Romans.
The criterion for claiming oneself to be a "Scillonian" typically relies on proof of being "island-born". Recent evidence from Essex University indicates that the young indigenous Cornish are increasingly underrepresented in the demographic profile, having been economically and socially displaced by older mainland-incomers. Census and subjective observations suggest that the ethnic makeup of the islands is almost exclusively white.
Sport
One continuing legacy of the isles' past is gig racing, wherein fast rowing boats ("gigs") with crews of six (or in one case, seven) race between the main islands. Gig racing has been said to derive from the race to collect salvage from shipwrecks on the rocks around Scilly, but the race was actually to deliver a pilot onto incoming vessels, to guide them through the hazardous reefs and shallows. (The boats are correctly termed "pilot gigs".)
The Isles of Scilly feature what is reportedly the smallest football league in the world. The league's two clubs, Woolpack Wanderers and Garrison Gunners, play each other sixteen times a season and compete for two cups as well as the league title. The league was a launching pad for the adidas "Dream Big" Campaign. The two share a ground, Garrison Field, but travel to the mainland for part of the year to play other non-professional clubs.
In December 2006, Sport England published a survey which revealed that residents of the Isles of Scilly were the most active in England in sports and other fitness activities. 32% of the population participate at least 3 times a week for 30 minutes.
Scilly is also popular scuba diving area.
Ornithology
The islands are famous for their birdwatching. Because Scilly is situated far into the Atlantic Ocean, American vagrant birds will make first European landfall in the archipelago. This fact attracts many birdwatchers each year, notably in the month of October.
Scilly is responsible for many firsts for Britain and never fails to produce good birds. It is particularly good at producing vagrant American Passerines (perching birds). If an extremely rare bird turns up the island will see a significant increase in numbers of birders. This type of birding, chasing after rare birds, is called 'twitching'.
In Literature
- The novel Unnatural Selection by Aaron Elkins is set on St. Mary's.
- Michael Morpurgo's book Why the whales came is set in the Scillies.