Effect of sun angle on climate
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Climate and the Weather
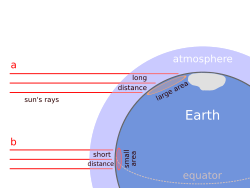
This diagram illustrated how sunlight is spread over a greater area in the polar regions. In addition to the density of incident light, the dissipation of light in the atmosphere is greater when it falls at a shallow angle.
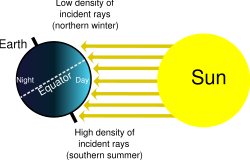
This is a diagram of the seasons. Regardless of the time of day (i.e. the Earth's rotation on its axis), the North Pole will be dark, and the South Pole will be illuminated; see also arctic winter.
The angle at which sunlight strikes the earth, which varies by location, time of day, and season, is an important factor in the amount of heat energy received at any location on the globe. Seasonal change in the angle of sunlight, caused by the tilt of the earth's axis, is the basic mechanism that results in warmer weather in summer than in winter (see Figure 1). (See also season.)
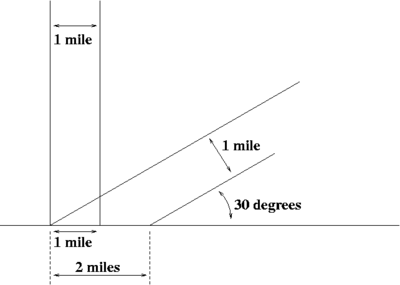
Geometry of sun angle
When sunlight shines on the earth at a lower angle (sun closer to the horizon), the energy of the sunlight is spread over a larger area, and is therefore weaker than if the sun is higher overhead and the energy is concentrated on a smaller area. (See Figure 2.)
Figure 1 shows the angle of sunlight striking the earth in the Northern and equator when the earth's northern axis is tilted away from the sun.
Figure 2 depicts a sunbeam one mile wide falling on the ground from directly overhead, and another hitting the ground at a 30° angle. Trigonometry tells us that the sine of a 30° angle is 1/2, whereas the sine of a 90° angle is 1. Therefore, the sunbeam hitting the ground at a 30° angle spreads the same amount of light over twice as much area (if we imagine the sun shining from the south at noon, the north-south width doubles; the east-west width does not). Consequently, the amount of light falling on each square mile is only half as much.
The sunbeam entering at the shallower angle must also travel twice as far through the Earth's atmosphere, which reflects some of the energy back into space.
Technical note
Heat energy is not received from the Sun. Radiant energy is received and this results in change in energy level of receiving bodies in Earth's domain. Different materials have different properties for transmitting back received energy in the form of heat energy at different rates. Concrete and tar for example are slow releasers. Most metals are fast releasers.