Constantine I
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Historical figures
| Constantine I | |
| Emperor of the Roman Empire | |
 Head of Constantine's colossal statue at the Capitoline Museums |
|
| Reign | 25 July 306 – 29 October 312 (hailed as Augustus in the West, officially made Caesar by Galerius with Severus as Augustus, by agreement with Maximian, refused relegation to Caesar in 309) 29 October 312 – 19 September 324 (undisputed Augustus in the West, senior Augustus in the empire) 19 September 324 – 22 May 337 (emperor of united empire) |
|---|---|
| Full name | Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus |
| Born | 27 February ca. 272 |
| Birthplace | Naissus (modern Niš, Serbia) |
| Died | 22 May 337 |
| Place of death | Nicomedia (modern Izmit, Turkey) |
| Predecessor | Constantius Chlorus |
| Successor | Constantine II, Constantius II and Constans |
| Wives | Minervina, died or divorced before 307 Fausta |
| Dynasty | Constantinian |
| Father | Constantius Chlorus |
| Mother | Helena |
| Children | Constantina, Helena, Crispus, Constantine II, Constantius II and Constans |
Flavius Valerius Aurelius Constantinus ( 27 February ca. 272 – 22 May 337), commonly known as Constantine I, Constantine the Great (among Roman Catholics), or Saint Constantine (among Eastern Orthodox and Byzantine Catholic Christians), was Roman Emperor from 306, and the undisputed holder of that office from 324 to his death. Best known for being the first Christian Roman Emperor, Constantine reversed the persecutions of his predecessor, Diocletian, and issued (with his co-emperor Licinius) the Edict of Milan in 313, which proclaimed religious toleration throughout the empire.
The Byzantine liturgical calendar, observed by the Eastern Orthodox Church and Eastern Catholic Churches of Byzantine rite, lists both Constantine and his mother Helena as saints. Although he is not included in the Latin Church's list of saints, which does recognize several other Constantines as saints, he is revered under the title "The Great" for his contributions to Christianity.
Constantine also transformed the ancient Greek colony of Byzantium into a new imperial residence, Constantinople, which would remain the capital of the Byzantine Empire for over a thousand years.
Early life
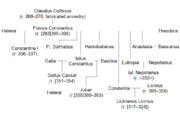
Constantine, named Flavius Valerius Constantinus, was born in the Moesian military city of Naissus ( Niš, Serbia) on the 27th of February of an uncertain year, probably near 272. His father was Flavius Constantius, a native of Moesia Superior (later Dacia Ripensis). Constantius was a tolerant and politically skilled man. Constantine probably spent little time with his father. Constantius was an officer in the Roman army in 272, part of the Emperor Aurelian's imperial bodyguard. Constantius advanced through the ranks, earning the governorship of Dalmatia from Emperor Diocletian, another of Aurelian's Illyrian companions, in 284 or 285. Constantine's mother was Helena, a Bithynian Greek of humble origin. It is uncertain whether she was legally married to Constantius or merely his concubine.
In July 285, Diocletian declared Maximian, another colleague from Illyricum, his co-emperor. Each emperor would have his own court, his own military and administrative faculties, and each would rule with a separate praetorian prefect as chief lieutenant. Maximian ruled in the West, from his capitals at Mediolanum (Milan, Italy) or Augusta Treverorum ( Trier, Germany), while Diocletian ruled in the East, from Nicomedia ( İzmit, Turkey). The division was merely pragmatic: the Empire was called "indivisible" in official panegyric, and both emperors could move freely throughout the Empire. In 288, Maximian appointed Constantius to serve as his praetorian prefect in Gaul. Constantius left Helena to marry Maximian's stepdaughter Theodora in 288 or 289.
Diocletian divided the Empire again in 293, appointing two Caesars (junior emperors) to rule over further subdivisions of East and West. Each would be subordinate to their respective Augustus (senior emperor) but would act with supreme authority in his assigned lands. This system would later be called the Tetrarchy. Diocletian's first appointee for the office of Caesar was Constantius; his second was Galerius, a native of Felix Romuliana ( Gamzigrad, Serbia). According to Lactantius, Galerius was a brutal, animalistic man. Although he shared the paganism of Rome's aristocracy, he seemed to them an alien figure, a semi-barbarian. On March 1, Constantius was promoted to the office of Caesar, and dispatched to Gaul to fight the rebels Carausius and Allectus. In spite of meritocratic overtones, the Tetrarchy retained vestiges of hereditary privilege, and Constantine became the prime candidate for future appointment as Caesar as soon as his father took the position. Constantine left the Balkans for the court of Diocletian, where he lived as his father's heir presumptive.
In the East
Constantine received a formidable education at Diocletian's court, where he learned Latin literature, Greek, and philosophy. The cultural environment in Nicomedia was open, fluid and socially mobile, and Constantine could mix with intellectuals both pagan and Christian. He may have attended the lectures of Lactantius, a Christian scholar of Latin in the city. Because Diocletian did not completely trust Constantius—none of the Tetrarchs fully trusted their colleagues—Constantine was held as something of a hostage, a tool to ensure Constantius' best behaviour. Constantine was nonetheless a prominent member of the court: he fought for Diocletian and Galerius in Asia, and served in a variety of tribunates; he campaigned against barbarians on the Danube in 296, and fought the Persians under Diocletian in Syria (297) and under Galerius in Mesopotamia (298–99). By late 305, he had become a tribune of the first order, a tribunus ordinis primi.
Constantine had returned to Nicomedia from the eastern front by the spring of 303, in time to witness the beginnings of Diocletian's " Great Persecution", the severest persecution of Christians in Roman history. In late 302, Diocletian and Galerius sent a messenger to the oracle of Apollo at Didyma with an inquiry about Christians. Constantine could recall his presence at the palace when the messenger returned, when Diocletian accepted his court's demands for universal persecution. On February 23, 303, Diocletian ordered the destruction of Nicomedia's new church, condemned its scriptures to the flame, and had its treasures seized. In the months that followed, churches and scriptures were destroyed, Christians were deprived of official ranks, and priests were imprisoned.
It is unlikely that Constantine played any role in the persecution. In his later writings he would attempt present himself as an opponent of Diocletian's "sanguinary edicts" against the "worshipers of God", but nothing indicates that he opposed it effectively at the time. Although no contemporary Christian challenged Constantine for his inaction during the persecutions, it remained a political liability throughout his life.
On May 1, 305, Diocletian, as a result of a debilitating sickness taken in the winter of 304–5, announced his resignation. In a parallel ceremony in Milan, Maximian did the same. Lactantius states that Galerius manipulated the weakened Diocletian into resigning, and forced him to accept Galerius' allies in the imperial succession. According to Lactantius, the crowd listening to Diocletian's resignation speech believed, until the very last moment, that Diocletian would choose Constantine and Maxentius ( Maximian's son) as his successors. It was not to be: Severus and Maximin were appointed, while Constantine and Maxentius were ignored.
Some of the ancient sources detail plots that Galerius made on Constantine's life in the months following Diocletian's abdication. They assert that Galerius assigned Constantine to lead an advance unit in a cavalry charge through a swamp on the middle Danube, made him enter into single combat with a lion, and attempted to kill him in hunts and wars. Constantine always emerged victorious: the lion emerged from the contest in a poorer condition than Constantine; Constantine returned to Nicomedia from the Danube with a Sarmatian captive to drop at Galerius' feet. It is uncertain how much these tales can be trusted.
In the West
Constantine's recognized the implicit danger in remaining at Galerius' court, where he was held as a virtual hostage. His career depended on being rescued by his father in the west. Constantius was quick to intervene. In the late spring or early summer of 305, Constantius requested leave for his son, to help him campaign in Britain. After a long evening of drinking, Galerius granted the request. Constantine's later propaganda describes how Constantine fled the court in the night, before Galerius could change his mind. He rode from post-house to post-house at high speed, mutilating every horse in his wake. By the time Galerius awoke the following morning, Constantine had fled too far to be caught. Constantine joined his father in Gaul, at Bononia ( Boulogne) before the summer of 305.
From Bononia they crossed the Channel to Britain and made their way to Eboracum (York), capital of the province of Britannia Secunda and home to a large military base. Constantine was able to spend a year in northern Britain at his father's side, campaigning against the Picts beyond Hadrian's Wall in the summer and autumn. Constantius' campaign, like that of Septimius Severus before it, probably advanced far into the north without achieving great success. Constantius had become severely sick over the course of his reign, and died on July 25, 306 in Eboracum (York). Before dying, he declared his support for raising Constantine to the rank of full Augustus. The Alamannic king Chrocus, a barbarian taken into service under Constantius, then proclaimed Constantine as Augustus. The troops loyal to Constantius' memory followed him in acclamation. Gaul and Britain quickly accepted his rule; Iberia, which had been in his father's domain for less than a year, rejected it.
Constantine sent Galerius an official notice of Constantius' death and his own acclamation. Along with the notice, he included a portrait of himself in the robes of an Augustus. The portrait was wreathed in bay. He requested recognition as heir to his father's throne, and passed off responsibility for his unlawful ascension on his army, claiming they had "forced it upon him". Galerius was put into a fury by the message; he almost set the portrait on fire. His advisers calmed him, and argued that outright denial of Constantine's claims would mean certain war. Galerius was compelled to compromise: He granted Constantine and the title "Caesar" rather than "Augustus" (The latter office went to Severus instead). Wishing to make it clear that he alone gave Constantine legitimacy, Galerius personally sent Constantine the emperor's traditional purple robes. Constantine accepted the decision, knowing that it would remove doubts as to his legitimacy.
Early rule
Constantine's share of the Empire consisted of Britain, Gaul, and Spain. He therefore commanded one of the largest Roman armies, stationed along the important Rhine frontier. After his promotion to emperor, Constantine remained in Britain, and secured his control in the northwestern dioceses. He completed the reconstruction of military bases begun under his father's rule, and ordered the repair of the region's roadways. He soon left for Augusta Treverorum ( Trier) in Gaul, the Tetrarchic capital of the northwestern Roman Empire. The Franks, after learning of Constantine's acclamation, invaded Gaul across the lower Rhine over the winter of 306–7. Constantine drove them back beyond the Rhine and captured two of their kings, Ascaric and Merogaisus. The kings and their soldiers were fed to the beasts of Trier's amphitheater in the adventus (arrival) celebrations that followed.
Constantine began a major expansion of Trier. He strengthened the circuit wall around the city with military towers and fortified gates, and began building a palace complex in the northeastern part of the city. To the south of his palace, he ordered the construction of a large formal audience hall, and a massive imperial bathhouse. Constantine sponsored many building projects across Gaul during his tenure as Emperor of the West, especially in Augustodunum ( Autun) and Arelate ( Arles). According to Lactantius, Constantine followed his father in following a tolerant policy towards Christianity. Although not yet a Christian, he probably judged it a more sensible policy than open persecution, and a way to distinguish himself from the "great persecutor" himself, Galerius. Constantine decreed a formal end to persecution, and returned to Christians all they had lost during the persecutions.
Because Constantine was still largely untried and had a hint of illegitimacy about him, he relied on his father's reputation in his early propaganda: the earliest panegyrics to Constantine give as much coverage to his father's deeds as to those of Constantine himself. Constantine's military skill and building projects soon gave the panegyrist the opportunity to comment favorably on the similarities between father and son, and Eusebius remarked that Constantine was a "renewal, as it were, in his own person, of his father's life and reign". Constantinian coinage, sculpture and oratory also shows a new tendency for disdain towards the "barbarians" beyond the frontiers. After Constantine's victory over the Alemanni, he minted a coin issue depicting weeping and begging Alemannic tribesmen—"The Alemanni conquered"—beneath the phrase "Romans' rejoicing". There was little sympathy for these enemies. As his panegyrist declared: "It is a stupid clemency that spares the conquered foe."
Maxentius' rebellion
Following Galerius' recognition of Constantine as emperor, his portrait was brought to Rome, as was customary. Maxentius mocked the portrait's subject as the son of a harlot, and lamented his own powerlessness. Maxentius, jealous of Constantine's authority, seized the title of emperor on October 28, 306. Galerius refused to recognize him, but failed to unseat him. During his first campaign against Maxentius, Severus' armies defected, and he was seized and imprisoned. Over the spring and summer of 307, he left Gaul for Britain to avoid any involvement in the Italian turmoil. Maximian, brought out of retirement by his son's rebellion, left for Gaul to confer with Constantine in late 307. He offered to marry his daughter Fausta to him, and elevate him to Augustan rank. In return, Constantine would reaffirm the old family alliance between Maximian and Constantius, and offer support to Maxentius' cause in Italy. Constantine accepted, and married Fausta in Trier in late summer 307. Constantine now gave Maxentius his meager support, offering Maxentius political recognition.
Constantine remained aloof from military conflict, however. Instead of sending his troops into a civil war, he sent them against Germanic tribes along the Rhine. In 308, he raided the territory of the Bructeri, and made a bridge across the Rhine at Colonia Agrippinensium (Cologne). In 310, he marched to the northern Rhine and fought the Franks. When not campaigning, he toured his lands advertising his benevolence, and supporting the economy and the arts. His refusal to participate in the war increased his popularity among his people, and strengthened his power base in the West. Maximian returned to Rome in the winter of 307–8, but soon fell out with his son. In early 309, after a failed attempt to usurp Maxentius' title, Maximian returned to Constantine's court.
On November 11, 308, Galerius called a general council at the military city of Carnuntum ( Petronell-Carnuntum, Austria) to resolve the instability in the western provinces. In attendance were Diocletian, briefly returned from retirement, Galerius, and Maximian. Maximian was forced to abdicate again and Constantine was again demoted to Caesar. Severus, one of Galerius' old military companions, was appointed Augustus of the west. The new system did not last long: Constantine refused to accept the demotion, and continued to style himself as Augustus on his coinage, even as other members of the Tetrarchy referred to him as a Caesar on theirs. Maximinus was frustrated that he had been turned over for promotion while the newcomer Licinius had been raised to the office of Augustus, and demanded that Galerius promote him. Galerius offered to call both Maximinus and Constantine "sons of the Augusti", but neither accepted the new title. By the spring of 310, Galerius was referring to both men as Augusti.
Maximian's rebellion

In 310, a dispossessed and power-hungry Maximian rebelled against Constantine while Constantine was away campaigning against the Franks. Maximian had been sent south to Arles with a contingent of Constantine's army, in preparation for any attacks by Maxentius in southern Gaul. He there announced that Constantine was dead, and took up the imperial purple. In spite of a large donative pledge to any who would support him as emperor, most of Constantine's army remained loyal to their emperor, and Maximian was soon compelled to leave. Constantine soon heard of the rebellion, abandoned his campaign against the Franks, and marched his army up the Rhine. At Cabillunum ( Chalon-sur-Saône), he moved his troops onto waiting boats to row down the slow waters of the Saône to the quicker waters of the Rhone. He disembarked at Lugdunum ( Lyon). Maximian fled to Massilia (Marseille), a town better able to withstand a long siege than Arles. It made little difference, however, as loyal citizens opened the rear gates to Constantine. Maximian was captured and reproved for his crimes. Constantine granted some clemency, but strongly encouraged his suicide. In July 310, Maximian hanged himself.
In spite of the earlier rupture in their relations, Maxentius was eager to present himself as his father's devoted son after his death. He began printing coins with his father's deified image, proclaiming his desire to avenge Maximian's death. Constantine initially presented the suicide as an unfortunate family tragedy. By 311, however, he was spreading another version. According to this, after Constantine had pardoned him, Maximian planned to murder Constantine in his sleep. Fausta learned of the plot and warned Constantine, who put a eunuch in his own place in bed. Maximian was apprehended when he killed the eunuch and was offered suicide, which he accepted. In addition to the propaganda, Constantine instituted a damnatio memoriae on Maximian, destroying all inscriptions referring to him and eliminating any public work bearing his image.
The death of Maximian necessitated a shift in Constantine's public image. He could no longer rely on his connection to the elder emperor Maximian, and needed a new source of legitimacy. In a speech delivered in Gaul on July 25, 310, the orator reveals a previously unknown dynastic connection to Claudius II, a third-century emperor famed for defeating the Goths and restoring order to the empire. Breaking away from tetrarchic models, the speech emphasizes Constantine's ancestral prerogative to rule, rather than principles of imperial equality. The new ideology expressed in the speech made Galerius and Maximian irrelevant to Constantine's right to rule. Indeed, the orator emphasizes ancestry to the exclusion of all other factors: "No chance agreement of men, nor some unexpected consequence of favour, made you emperor," the orator declares to Constantine.
The oration also moves away from the religious ideology of the Tetrarchy, with its focus on twin dynasties of Jupiter and Hercules. Instead, the orator proclaims that Constantine experienced a divine vision of Apollo and Victory granting him laurel wreaths of health and a long reign. In the likeness of Apollo Constantine recognized himself as the saving figure to whom would be granted "rule of the whole world", as the poet Virgil had once foretold. The oration's religious shift is paralleled by a similar shift in Constantine's coinage. In his early reign, the coinage of Constantine advertised Mars as his patron. From 310 on, Mars was replaced by Sol Invictus, a god conventionally identified with Apollo. There is little reason to believe that either the dynastic connection or the divine vision are anything other than fiction, but their proclamation strengthened Constantine's claims to legitimacy and increased his popularity among the citizens of Gaul.
Civil wars
War against Maxentius
|
|||||
By the middle of 310 Galerius had had become too ill to involve himself in imperial politics. As his last political act, Galerius decided to rescind his failed policies of persecution. In a letter to his provincials posted in Nicomedia on April 30, 311, Galerius proclaimed an end to the persecutions, and a resumption of official religious toleration. He died soon after. Galerius' death destabilized what remained of the tetrarchic system. Maximinus mobilized against Licinius, and seized Asia Minor. Licinius and Maximinus arranged a temporary peace on the Bosphorus soon thereafter. While Constantine toured Britain and Gaul, Maxentius prepared for war. He fortified northern Italy, and strengthened his support in the Christian community by allowing it to elect a new Bishop of Rome, Eusebius.
Maxentius' rule was nevertheless insecure. His early support dissolved in the wake of heightened tax rates and depressed trade; riots broke out in Rome and Carthage; and Domitius Alexander was able to briefly usurp his authority in Africa. By 312, he was a man barely tolerated, not one actively supported, even among Christian Italians. In the summer of 311, Maxentius mobilized against Constantine while Licinius was occupied with affairs in the East. He declared war on Constantine, vowing to avenge his father's "murder". Constantine, in an attempt to prevent Maxentius from forming a hostile alliance with Licinius, forged his own alliance with the man over the winter of 311–12 by offering to him his sister Constantia in marriage. Maximin considered Constantine's arrangement with Licinius an affront to his authority. In response, he sent ambassadors to Rome, offering political recognition to Maxentius in exchange for a military support. Maxentius accepted. According to Eusebius, inter-regional travel became impossible, and there was military buildup everywhere. There was "not a place where people were not expecting the onset of hostilities every day".

Constantine's advisers and generals cautioned against preemptive attack on Maxentius; even his soothsayers recommended against it, stating that the sacrifices had produced unfavorable omens. Constantine, with a spirit that left a deep impression on his followers, inspiring some to believe that he had some form of supernatural guidance, ignored all these cautions, and attacked Maxentius without a casus belli. Early in the spring of 312, Constantine crossed the Cottian Alps with a quarter of his total army, approximately 40,000 men. He first came to Segusium ( Susa, Italy), a heavily fortified town containing a military garrison, which shut its gates to him. Constantine ordered his forces set its gates on fire, scaled its walls, and took the town quickly. Constantine forbade the plunder of the town, and advanced into northern Italy.
At the approach to the west of the important city of Augusta Taurinorum (Turin, Italy), Constantine encountered a large force of heavily armed Maxentian cavalry. In the ensuing battle Constantine encircled Maxentius' cavalry, flanked them with his own cavalry, and dismounted them with blows from his soldiers' iron-tipped clubs. Constantine's armies emerged victorious. Turin refused to give refuge to Maxentius' retreating forces, opening its gates to Constantine instead. Other cities of the north Italian plain sent Constantine embassies of congratulation for his victory. He moved on to Milan, where he was met with open gates and jubilant rejoicing. Constantine rested his army in Milan until mid-summer 312, when he moved on to Brixia ( Brescia).
Brescia's army was easily dispersed, and Constantine quickly advanced to Verona, where a large Maxentian force was camped. Ruricius Pompeianus, general of the Veronese forces and Maxentius' praetorian prefect, was in a strong defensive position. Constantine sent a small force to cross the river at a point north of the city. Ruricius sent a large detachment to counter Constantine's expeditionary force, but it was defeated. Constantine's forces successfully surrounded the town and laid siege. Ruricius gave Constantine the slip and returned with a larger force to oppose Constantine. Constantine refused to let up on the siege, and sent only a small force to oppose him. In the desperately-fought encounter that followed, Ruricius was killed and his army destroyed. Verona surrendered soon afterwards, followed by Aquileia, Mutina ( Modena), and Ravenna. The road to Rome was now wide open to Constantine.
Maxentius prepared for the same type of war he had waged against Severus and Galerius: he sat in Rome and prepared for a siege. He still controlled Rome's praetorian guards, was well-stocked with African grain, and was surrounded on all sides by the seemingly-impregnable Aurelian Walls. He ordered all bridges across the Tiber cut, reportedly on the counsel of the gods, and left the rest of central Italy undefended; Constantine secured that region's support without challenge. Constantine progressed slowly, along the Via Flaminia, allowing the weakness of Maxentius to draw his regime further into turmoil. Maxentius' support continued to weaken: at chariot races on October 27, the crowd openly taunted Maxentius, shouting that Constantine was invincible. Maxentius, no longer certain that he would emerge from a siege victorious, built a temporary boat bridge across the Tiber in preparation for a field battle against Constantine. On October 28, 312, the sixth anniversary of his reign, he approached the keepers of the Sibylline Books for guidance. The keepers found in them a prophecy stating that, on that very day, "the enemy of the Romans" would die. Maxentius advanced north to meet Constantine in battle.
Maxentius organized his forces—still twice the size of Constantine's—in long lines facing the battle plain, with their backs to the river. When Constantine's army made its appearance, some of its soldiers bore unusual markings on their shields: instead of the traditional pagan standards, a new sign, the labarum, was mounted. According to Lactantius, Constantine was visited by a dream the night before the battle, wherein he was advised "to mark the heavenly sign of God on the shields of his soldiers...by means of a slanted letter X with the top of its head bent round, he marked Christ on their shields." Eusebius describes another version, where, while marching at midday, "he saw with his own eyes in the heavens a trophy of the cross arising from the light of the sun, carrying the message, Conquer By This". During the following night, in a dream, Christ appeared with the heavenly sign and told him to make standards for his army in that form. Although Eusebius is vague about when and where this event took place, it enters his narrative before the war against Maxentius begins. Eusebius describes the sign as Chi (Χ) traversed by Rho (Ρ), or ☧. The Eusebian description of the vision has been explained as an example of the meteorological phenomenon known as the " solar halo", which can produce similar effects.
Constantine deployed his own forces in along the whole length of Maxentius' line. He ordered his cavalry to charge, and they broke Maxentius' cavalry. He then sent his infantry against Maxentius' infantry, pushing many into the Tiber where they were slaughtered and drowned. The battle was brief: Maxentius' troops were broken before the first charge. Maxentius' horse guards and praetorians initially held their position, but broke under the force of a Constantinian cavalry charge; they also broke ranks and fled to the river. Maxentius rode with them, and attempted to cross the bridge of boats, but he was pushed by the mass of his fleeing soldiers into the Tiber, and drowned.
Constantine entered Rome on October 29. He staged a grand adventus in the city, and was met with popular jubilation. Maxentius' body was fished out of the Tiber and decapitated. His head was paraded through the streets for all to see. After the ceremonies, Maxentius' disembodied head was sent to Carthage, after which Africa gave no further resistance. He entered as a Christian: unlike his predecessors, he neglected to make the trip to the Capitoline Hill and perform customary sacrifices at the Temple of Jupiter. He did, however, choose to honour the Senatorial Curia with a visit, where he promised to restore its ancestral privileges and give it a secure role in his reformed government: there would be no revenge against Maxentius' supporters. In response, the Senate decreed him "title of the first name", which meant his name would be listed first in all official documents, and acclaimed him as "the greatest Augustus". He issued decrees returning property lost under Maxentius, recalling political exiles, and releasing Maxentius' imprisoned opponents.
In an extensive propaganda campaign followed: Maxentius' image was systematically purged from all public places. Maxentius was written up as a " tyrant", and set against an idealized image of the "liberator", Constantine. Eusebius, in his later works, is the best representative of this strand of Constantinian propaganda. Constantine also attempted to remove Maxentius' influence on Rome's urban landscape. All structures built by Maxentius were re-dedicated to Constantine, including the Temple of Romulus and the Basilica of Maxentius. Where he did not overwrite Maxentius' achievements, he upstaged them: the Circus Maximus was redeveloped so that its total seating capacity was twenty-five times larger than that of Maxentius' racing complex on the Via Appia. Maxentius' strongest supporters in the military were neutralized when the Praetorian Guard and Imperial Horse Guard (equites singulares) were disbanded. Their tombstones were ground up and put to use in a basilica on the Via Labicana. Early in Constantine's reign, the former base of the Imperial Horse Guard was chosen for redevelopment into the Lateran Basilica. Art historian Richard Krautheimer dated the event to November 9, 312, barely two weeks after Constantine captured the city. The Legio II Parthica was removed from Alba ( Albano Laziale), and the remainder of Maxentius' armies were sent to do frontier duty on the Rhine.
Wars against Licinius
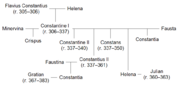
In the following years, Constantine gradually consolidated his military superiority over his rivals in the crumbling Tetrarchy. In 313, he met Licinius in Milan to secure their alliance by the marriage of Licinius and Constantine's half-sister Constantia. During this meeting, the emperors agreed on the so-called Edict of Milan (which, in its surviving forms, was neither an edict nor issued in Milan), officially granting full tolerance to all religions in the Empire. The document had special benefits for Christians, legalizing their religion and granting them restoration for all property seized during Diocletian's persecution. It repudiates past methods of religious coercion, accepting religious plurality and using only general terms—"Divinity" and "Supreme Divinity", summa divinitas—avoiding any exclusive specificity. The conference was cut short, however, when news reached Licinius that his rival Maximinus Daia had crossed the Bosporus and invaded Licinian territory. Licinius departed and eventually defeated Maximinus, gaining control over the entire eastern half of the Roman Empire. Relations between the two remaining emperors deteriorated, though, and either in 314 or 316, Constantine and Licinius fought against one another in the war of Cibalae, with Constantine being victorious. They clashed again in the Battle of Campus Ardiensis in 317, and agreed to a settlement in which Constantine's sons Crispus and Constantine II, and Licinius' son Licinianus were made caesars.
In the year 320, Licinius reneged on the religious freedom promised by the Edict of Milan in 313 and began another persecution of the Christians. It became a challenge to Constantine in the west, climaxing in the great civil war of 324. Licinius, aided by Goth mercenaries, represented the past and the ancient Pagan faiths. Constantine and his Franks marched under the Christian standard of the labarum, and both sides saw the battle in religious terms. Supposedly outnumbered, but fired by their zeal, Constantine's army emerged victorious in the Battle of Adrianople. Licinius fled across the Bosphorus and appointed Martius Martinianus, the commander of his bodyguard, as Caesar, but Constantine next won the Battle of the Hellespont, and finally the Battle of Chrysopolis on 18 September 324. Licinius and Martinianus surrendered to Constantine at Nicomedia on the promise their lives would be spared: they were sent to live as private citizens in Thessalonica and Cappadocia respectively, but in 325 Constantine accused Licinius of plotting against him and had them both arrested and hanged; Licinius's son (the son of Constantine's half-sister) was also eradicated. Thus Constantine became the sole emperor of the Roman Empire.
Later rule
Foundation of Constantinople
Licinius' defeat represented the passing of old Rome, and the beginning of the role of the Eastern Roman Empire as a centre of learning, prosperity, and cultural preservation. Constantine rebuilt the city of Byzantium, which was renamed Constantinopolis ("Constantine's City" or Constantinople in English), and issued special commemorative coins in 330 to honour the event. He provided the "Second Rome" with a Senate and civic offices similar to those of Rome. The new city was protected by the alleged True Cross, the Rod of Moses and other holy relics, though a cameo now at the Hermitage Museum also represented Constantine crowned by the tyche of the new city. The figures of old gods were either replaced or assimilated into a framework of Christian symbolism. Constantine built the new Church of the Holy Apostles on the site of a temple to Aphrodite. Generations later there was the story that a Divine vision led Constantine to this spot, and an angel no one else could see, led him on a circuit of the new walls. The capital would often be compared to the 'old' Rome as Nova Roma Constantinopolitana, the "New Rome of Constantinople").
Religious policy
Constantine is perhaps best known for being the first Christian Roman Emperor. His reign was a turning point for the Christian Church. In 313 Constantine announced toleration of Christianity in the Edict of Milan, which removed penalties for professing Christianity (under which many had been martyred in previous persecutions of Christians) and returned confiscated Church property. Though a similar edict had been issued in 311 by Galerius, then senior emperor of the Tetrarchy, Constantine's lengthy rule, conversion, and patronage of the Church redefined the status of Christianity in the empire. From the beginning, Christianity was regarded as completely pacifistic, due to a strict interpretation of the Bible as well as constant persecution by the Roman Empire. However, when Christianity became the official religion of the empire "all of Christianity began to embrace just war theory, as an attempt to be realistic about evil and harm-doing", a critical transition for the church. Another consequence of Christianity being the state religion was that clergy members were given preferred status and exempted from military service and forced labor. There was a growing divide between clergy and laity as conversions were often more about socioeconomic status rather than faith. Converts were baptized in order to abuse Christianity for political influence, a problem unheard of before Constantine, when converts to Christianity willingly risked their life for their faith.
Scholars debate whether Constantine adopted his mother St. Helena's Christianity in his youth, or whether he adopted it gradually over the course of his life. Constantine was over 40 when he finally declared himself a Christian. Constantine however still maintained the title of Pontifex Maximus, which emperors bore as heads of the pagan priesthood. Writing to Christians, Constantine made clear that he believed he owed his successes to the protection of the Christian High God alone. Throughout his rule, Constantine supported the Church financially, built various basilicas, granted privileges (e.g. exemption from certain taxes) to clergy, promoted Christians to high ranking offices, and returned property confiscated during the Great Persecution of Diocletian. His most famous building projects include the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and Old Saint Peter's Basilica.
The reign of Constantine established a precedent for the position of the Christian Emperor in the Church; Constantine considered himself responsible to God for the spiritual health of his subjects, and thus he had a duty to maintain orthodoxy. The emperor ensured that God was properly worshipped in his empire; what proper worship consisted of was for the Church to determine. In 316, Constantine acted as a judge in a North African dispute concerning the heresy of Donatism. After making a decision against the Donatists, Constantine led an army of Christians against Christians. After 300 years of pacifism, this was the first intra-Christian persecution. More significantly, in 325 he summoned the Council of Nicaea, effectively the first Ecumenical Council (unless the Council of Jerusalem is so classified), to deal mostly with the heresy of Arianism. Constantine also enforced the prohibition of the First Council of Nicaea against celebrating Easter on the day before the Jewish Passover (14 Nisan) (see Quartodecimanism and Easter controversy).
Constantine instituted several legislative measures which had an impact on Jews. They were forbidden to own Christian slaves or to circumcise their slaves. Conversion of Christians to Judaism was outlawed. Congregations for religious services were restricted, but Jews were allowed to enter Jerusalem on Tisha B'Av, the anniversary of the destruction of the Temple.
Executions of Crispus and Fausta
On some date between May 15 and June 17, 326, Constantine had his eldest son Crispus seized and put to death by "cold poison" at Pola ( Pula, Croatia). In July, Constantine had his wife, the Empress Fausta, killed at the behest of his mother, Helena. Fausta was left to die in an over-heated bath. Their names were wiped from the face of many inscriptions, references to their lives in the literary record were erased, and the memory of both was condemned. Eusebius, for example, edited praise of Crispus out of later copies of his Historia Ecclesiastica, and his Vita Constantini contains no mention of Fausta or Crispus at all. Few ancient sources are willing to discuss possible motives for the events; those few that do offer unconvincing rationales, are of later provenance, and are generally unreliable. At the time of the executions, it was commonly believed that the Empress Fausta was either in an illicit relationship with Crispus, or was spreading rumors to that effect. A popular myth arose, modified to allude to Hippolytus– Phaedra legend, with the suggestion that Constantine killed Crispus and Fausta for their immoralities. One source, the largely fictional Passion of Artemius, probably penned in the eighth century by John of Damascus, makes the legendary connection explicit. As an interpretation of the executions, the myth rests on only "the slimmest of evidence": sources that allude to the relationship between Crispus and Fausta are late and unreliable, and the modern suggestion that Constantine's "godly" edicts of 326 and the irregularities of Crispus are somehow connected rests on no evidence at all. An additional story goes that Fausta wanted to kill Crispus to ensure that her children would receive the Imperial throne. Therefore she told Constantine that Crispus had attempted to rape her, and bribed several senators to collaborate the story. Constantine was obligated by Roman Law to execute his son, as these charges were as serious as treason in Roman times. Hence, Constantine reluctantly, and sadly, executed his son. Later, his mother Helena heard of what had taken place, and investigated the event. She discovered that Fausta had bribed the senators, and told Constantine. For her treason, Fausta was executed in the gentlest way known at the time; she was locked in a bath. (This process would make the criminal pass out far before they were dead, and as such would feel no pain). After this entire event Constantine was so depressed that he never returned to the western half of the empire in his lifetime.
Sickness and death
Eusebius of Caesarea's account resumes following the abortive Persian campaign, with Constantine set about building a martyrion for the apostles in Constantinople, and, within it, a final resting-place for himself. In the course of one Feast of Easter, Constantine fell seriously ill. He left Constantinople for the hot baths near his mother's city of Helenopolis (Altinova), on the southern shores of the Gulf of İzmit. There, in a church his mother built in honour of Lucian the Apostle, he prayed, and there he realized that he was dying. Seeking purification, he became a catechumen, and attempted a return to Constantinople, making it only as far as a suburb of Nicomedia. He summoned the bishops, and told them of his hope to be baptized in the River Jordan, where Christ was written to have been baptized. He requested the baptism right away, promising to live a more Christian life should he live through his illness. The bishops, Eusebius records, "performed the sacred ceremonies according to custom". He chose the Arianizing bishop Eusebius of Nicomedia, bishop of the city where he lay dying, as his baptizer. In postponing his baptism, he followed one custom at the time which postponed baptism until old age or death. It was thought Constantine put off baptism as long as he did so as to be absolved from as much of his sin as possible. Constantine died soon after at a suburban villa called Achyron, on the last day of the fifty-day festival of Pentecost directly following Easter, on May 22, 337.

Although Constantine's death follows the conclusion of the Persian campaign in Eusebius's account, most other sources report his death as occurring in its middle. Emperor Julian, writing in the mid-350s, observes that the Sassanians escaped punishment for their ill-deeds, because Constantine died "in the middle of his preparations for war". Similar accounts are given in the Origo Constantini, an anonymous document composed while Constantine was still living, and which has Constantine dying in Nicomedia; the Historiae abbreviatae of Sextus Aurelius Victor, written in 361, which has Constantine dying at an estate near Nicomedia called Achyrona while marching against the Persians; and the Breviarium of Eutropius, a handbook compiled in 369 for the Emperor Valens, which has Constantine dying in a nameless state villa in Nicomedia. From these and other accounts, some have concluded that Eusebius's Vita was edited to defend Constantine's reputation against what Eusebius saw as a less congenial version of the campaign.
Following his death, his body was transferred to Constantinople and buried in the Church of the Holy Apostles there. He was succeeded by his three sons born of Fausta, Constantine II, Constantius II and Constans. A number of relatives were killed by followers of Constantius. He also had two daughters, Constantina and Helena, wife of Emperor Julian.
Legacy
Although he earned his honorific of "The Great" ("Μέγας") from Christian historians long after he had died, he could have claimed the title on his military achievements and victories alone. In addition to reuniting the Empire under one emperor, Constantine won major victories over the Franks and Alamanni in 306–8, the Franks again in 313–14, the Visigoths in 332 and the Sarmatians in 334. In fact, by 336, Constantine had actually reoccupied most of the long-lost province of Dacia, which Aurelian had been forced to abandon in 271. At the time of his death, he was planning a great expedition to put an end to raids on the eastern provinces from the Persian Empire.
The Byzantine Empire considered Constantine its founder and the Holy Roman Empire reckoned him among the venerable figures of its tradition. In the later Byzantine state, it had become a great honour for an emperor to be hailed as a "new Constantine". Ten Emperors, including the last emperor of Byzantium, carried the name. At the court of Charlemagne, the selected use of monumental Constantinian forms lent expression to conception of Charlemagne as Constantine's successor and equal. Constantine acquired a mythic role as a warrior against "heathens". The motif of the Romanesque equestrian, the mounted figure in the posture of a triumphant Roman emperor, came to be used as a visual metaphor in statuary in praise of local benefactors. The name "Constantine" itself enjoyed renewed popularity in western France in the eleventh and twelfth centuries. Most Eastern Christian churches consider Constantine a saint (Άγιος Κωνσταντίνος, Saint Constantine). In the Byzantine Church he was called isapostolos (Ισαπόστολος Κωνσταντίνος)—an equal of the Apostles.
During his life and those of his sons, Constantine's was presented as a paragon of virtue. Even pagans like Praxagoras of Athens and Libanius showered him with praise. When the last of his sons died in 361, his nephew Julian the Apostate wrote the satire Symposium, or the Saturnalia. The work stigmatized Constantine as inferior to the great pagan emperors, given over to luxury and greed. Following Julian, Eunapius of Sardis began the tradition that blamed Constantine for weakening the Empire through his indulgence to the Christians. In medieval times, when the Roman Catholic Church was dominant, Catholic historians presented Constantine as an ideal ruler, the standard against which any king or emperor could be measured. The Renaissance rediscovery of anti-Constantinian sources prompted a re-evaluation of Constantine's career. The German humanist Johann Löwenklau, discoverer of Zosimus' writings, published a Latin translation thereof in 1576. He included a preface that argued for Zosimus' picture of Constantine was superior to that offered by Eusebius and the church historians, and damned Constantine as a tyrant. Cardinal Caesar Baronius, a man of the Counter-Reformation, criticized Zosimus, favoring Eusebius' account of the Constantinian era. Baronius' Life of Constantine (1588) presents Constantine as the model of a Christian prince. Edward Gibbon, aiming to unite the two extremes of Constantinian scholarship, offered a portrait of Constantine built on the contrasted narratives of Eusebius and Zosimus.
Modern interpretations of Constantine's rule begin with Jacob Burckhardt's The Age of Constantine the Great (1853). Burckhardt's Constantine is a scheming secularist, a politician who manipulates all parties in a quest to secure his own power. Henri Grégoire, writing in the 1930s, followed Burckhardt's evaluation of Constantine. For Grégoire, Constantine only developed an interest in Christianity after witnessing its political usefulness. Grégoire became a strong of the authenticity of Eusebius' writings, and postulated a pseudo-Eusebius to assume responsibility for the vision and conversion narratives of Eusebius' Vita Constantini. Otto Seeck (Geschichte des Untergangs der antiken Welt (Stuttgart, 1920–23)) and André Piganiol (L'empereur Constantin (Paris, 1932)) wrote against this historiographic tradition. Seeck presented Constantine as a sincere war hero, whose ambiguities were the product of his own simple inconsistency. Piganiol's Constantine is a philosophical monotheist, a child of his era's religious syncretism. Related histories by A.H.M. Jones (Constantine and the Conversion of Europe (London, 1949)) and Ramsay MacMullen (Constantine (New York, 1969)) gave portraits of a less visionary, and more impulsive, Constantine.
These later accounts were more willing to present Constantine as a genuine convert to Christianity. Beginning with Norman H. Baynes' Constantine the Great and the Christian Church (London, 1929) and reinforced by Andreas Alföldi's The Conversion of Constantine and Pagan Rome (Oxford, 1948), a historiographic tradition developed which presented Constantine as a committed Christian. T.D. Barnes' seminal Constantine and Eusebius (Cambridge, MA, 1981), represents the culmination of this trend. Barnes' Constantine experienced a radical conversion, which drove him on a personal crusade to convert his empire. The trend reaches its zenith in T.G. Elliott's The Christianity of Constantine the Great (Bronx, NY, 1996). Elliott portrays Constantine as a committed Christian from early childhood.
Donation of Constantine
Latin Rite Catholics of the Middle Ages considered it inappropriate that Constantine was baptized only on his death-bed and by a bishop of questionable orthodoxy, viewing it as a snub to the authority of the Papacy. Hence, by the early fourth century, a legend had emerged that Pope Sylvester I (314–35) had cured the pagan Emperor from leprosy. According to this legend, Constantine was soon baptized, and began the construction of a church in the Lateran Palace. In the eighth century, most likely during the pontificate of Stephen II (752–7), a document called the " Donation of Constantine" first appeared, in which the freshly converted Constantine hands the temporal rule over "the city of Rome and all the provinces, districts, and cities of Italy and the Western regions" to Stephen and his successors. In the High Middle Ages, this document was used and accepted as the basis for the Pope's temporal power, though it was denounced as a forgery by Emperor Otto III and lamented as the root of papal worldliness by the poet Dante Alighieri. The 15th century philologist Lorenzo Valla proved the document was indeed a forgery.
Geoffrey of Monmouth's Historia
Because of his fame and his being proclaimed Emperor on the territory of Great Britain, Constantine was later also considered a British King. In the 11th century, the English writer Geoffrey of Monmouth published a fictional work called Historia Regum Britanniae, in which he narrates the supposed history of the Britons and their kings from the Trojan War, King Arthur and the Anglo-Saxon conquest. In this work, Geoffrey claimed that Constantine's mother Helena was actually the daughter of " King Cole", the mythical King of the Britons and eponymous founder of Colchester. A daughter for King Cole had not previously figured in the lore, at least not as it has survived in writing, and this pedigree is likely to reflect Geoffrey's desire to create a continuous line of regal descent. It was indecorous, Geoffrey considered, that a king might have less-than-noble ancestors. Geoffrey also said that Constantine was proclaimed " King of the Britons" at York, rather than Roman Emperor.