Cockatiel
2008/9 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Birds
| Cockatiel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Male  Female
|
||||||||||||||||
| Conservation status | ||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||||
| Nymphicus hollandicus ( Kerr, 1792) |
||||||||||||||||
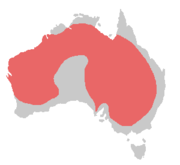 Cockatiel range (in red; all-year resident)
|
||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms | ||||||||||||||||
|
Psittacus hollandicus Kerr, 1792 |
The Cockatiel Parakeet (Nymphicus hollandicus), also known as the Quarrion and the Weero, is a diminutive cockatoo endemic to Australia and prized as a household pet. They are relatively easy to breed and keep in captivity and they are kept throughout the world as pets.
The only member of the genus Nymphicus, the Cockatiel has previously been considered a crested parrot or small cockatoo. However, more recent molecular studies have settled the debate, showing their closest relatives to be the black cockatoos of the genus Calyptorhynchus. They are hence now classified as the smallest of the Cacatuidae (cockatoo family). Cockatiels are natively found across the outback regions of inland Australia, and favour the Australian wetlands, scrublands, and bush lands.
Taxonomy
The Cockatiel was originally described by Scottish writer and naturalist Robert Kerr in 1792 as Psittacus hollandicus, before being placed in its own genus Nymphicus by Wagler in 1832. Placed in its own genus, the Cockatiel's scientific name Nymphicus hollandicus reflects the experience of one of the earliest groups of Europeans to see Cockatiels in their native habitat. Travelers thought they were so beautiful that they named them after mythical nymphs. (Nymphicus literally means "little nymph.") The species name refers to New Holland, an old name for Australia
Its biological relationship had long been disputed; it is placed into a monotypic subfamily Nymphicinae but had sometimes in the past been included among the Platycercinae, the broad-tailed Parakeets. This issue has now been settled with molecular studies. Mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequence data places it amongst the Calyptorhynchinae (dark cockatoos) subfamily. The unique, Parakeet morphological feature is a consequence of the decrease in size and accompanying change of ecological niche.
Sequence analysis of intron 7 of the nuclear ?- fibrinogen gene, on the other hand, indicates that it may yet be distinct enough as to warrant recognition of the Nymphicinae rather than inclusion of the genus in the Calyptorhynchinae.
The Cockatiel Parakeet (Parakeet meaning LONG-tailed Parrot) nicknamed Cockatiel is now biologically classified as a genuine member of Cacatuidae on account of sharing all of the Cockatoo family's biological features. Namely; the erectile crest, a gallbladder, powder down, suppressed cloudy-layer (enabling Lories, Lorikeets (long-tailed Lories), Parakeets & typical Parrot species display of structural colours such as aquas, blues, greens, purples & turquoises), and facial feathers covering the sides of the beak, all of which are rarely found outside the Cacatuidae family.
Portrayal
The Cockatiel's distinctive erectile crest expresses the animal's state of being. (Some say "emotional state.") The crest is dramatically vertical when the cockatiel is startled or excited, gently oblique in its neutral or relaxed state, and flattened close to the head when the animal is angry or defensive. The crest is also held flat but protrudes outward in the back when the cockatiel is trying to appear alluring or flirtatious. In contrast to most Cockatoos, the Cockatiel has long tail feathers roughly making up half of its total length. At 300 mm to 330 mm (12 to 13 ins), the Cockatiel is the smallest & only Parakeet (meaning LONG-tailed Parrot) type of Cockatoo species. The latter ranging between 300 mm to 600 mm (12-24 in) in length.
The "Normal Grey," or "Wild-type" cockatiel's plumage is primarily grey with prominent white flashes on the outer edges of each wing. The face of the male is yellow or white, while the face of the female is primarily grey or light grey, and both genders feature a round orange area on both ear areas, often referred to as "cheek patches." This orange colouration is generally vibrant in adult males, and often quite muted in females. Visual sexing is often possible with this variant of the bird.
Distribution and habitat
Cockatiels are native only to Australia where they are found largely in arid or semi-arid country, but always near water. Sometimes hundreds will flock around a single such body of water. To farmers' dismay, they often eat cultivated crops. They are absent from the most fertile southwest and southeast corners of the country, the deepest Western Australian deserts, and Cape York Peninsula. They are the only Cockatoo species which can sometimes reproduce in the end of their first year.
Lifespan
The Cockatiel's lifespan in captivity is generally given as 15-20 years, though it is sometimes given as short as 10-15 years, and there are reports of Cockatiels living as long as 30 years, the oldest confirmed specimen reported being 35 years old when it died. A cockatiel lived to be 27 years old in Manchester, UK. Diet and exercise, much like in humans, are often major determining factors in cockatiel lifespan. Again, breeders dispute the best diet for increasing the longevity of the cockatiel lifespan.
Aviculture
Cockatiels are generally regarded as good pets having a "sweet" demeanor, though this is by no means a guarantee. Like most other pets, the manner in which the animal is raised, handled, and kept has a profound effect on the temperament of the animal. Some birds are quite gregarious and sociable while others can be shy, retreating to the back of the cage when an unfamiliar figure appears.
Generally, well-socialised birds are gentle and friendly. Some cockatiels enjoy physical contact, lending themselves well to domestication. Many cockatiel owners develop regular bonding rituals with their animals, engaging in preening, scratching, and even petting. Cockatiels which are hand-fed and purchased from a young age are more readily suited for physical contact.
Some birds will emit a distinctive "hiss" when irritated, retreating rapidly or defending with pecking bites, which can be relatively strong for their size. This "hiss" is a form of mimicry used in a defensive attempt to confuse the cockatiel's most common predator, the snake.
Cockatiels do have a reputation for being quite noisy and demanding of the attention of their owners on a regular basis. Their vocalisations range from ginger cheeps to piercing cries.
They can be made more secure (in the mood for singing/mimicry, playing, etc) when they have a consistent few hours of quality time per day with a person or in a person's company and a good night's sleep. Twelve hours of sleep at least is required for a happy pet, sleep taken away can cause sickness and grumpy pets. Cockatiels living in a household with late sleepers should be taken to a quiet spare room where sun doesn't shine into in the morning or if you live in a small house or unit putting your pet in the bathroom is a good idea as long as you shut the toilet lid. Otherwise quiet birds will frequently make contact calls with their owners, calls that sometimes can be quite loud if the person is out of sight. Cockatiels can grow so attached to their owners that they may try to 'protect' them from anyone that tries to come near them, such as a partner or family member, by biting or hissing. This happens especially if cockatiels are kept in bedrooms or other rooms that are not generally shared by everyone in the family, because cockatiels perceive those rooms as their own personal territory. By keeping cockatiels in a shared household room, they are exposed to all family members equally and will not favour one person and feel the need to defend him or her as much. Cockatiels must be acquainted with the entire family, in order to assure even temperament toward all. A scared cockatiel will choose flight over fight most of the time, thus creating a chance for injury (i.e. flying into a glass door). Their popularity as pets is in part because of their calm and timid temperament, to the point that they can even be bullied by smaller but more confident birds such as Budgerigars. Budgerigars and other smaller birds may choose to pick at cockatiels' feet causing lost toes. Great care and supervision should be provided when mixing cockatiels with other birds. It is not uncommon at all for a larger or smaller bird to maim the cockatiel, creating life-long disabilities and potentially life threatening injuries. However, some cockatiels will defend themselves.
Cockatiels don't necessarily make good pets for young children because they startle easily with loud or unexpected sounds and can bite out of fear of sudden hand movements near and above their heads. The shoulders of children are small and unstable perches compared with those of adults, and forcing the bird to use an uncomfortable place to stand may lead to the bird disliking the child. Once bonded with their owners, they will often cuddle and play, pushing their head against hands or faces, and may nibble at fingers for attention to get a scratch on the head and neck. Cockatiels, like almost all other parrots, love to chew paper and can destroy objects (like cardboard, books, magazines, wicker baskets, etc) left unattended. Most cockatiels enjoy looking at themselves in mirrors and will engage in the activity for hours. Cockatiels that are exposed to mirrors perceive their reflections as their mates. This can induce very aggressive behaviour, and upon seeing themselves once, they are likely to experience anxiety until they find the mirror again.
The Cockatiel, along with the Budgerigar, is among the most popular pet bird species. Today all Cockatiels available in the pet trade are captive-bred, as Australia no longer permits the export of native wildlife, whether endangered or not.
Vocalisation
Although cockatiels are part of the parrot order, they are better at imitating whistles than speech. Although they can learn words, the only understandable parts of the words are the inflections, while the consonants are not easily discernible. Their whistles and other mimicking sounds such as 'lip-smacking' and 'tutting' are almost perfect imitations of the sounds their owners make.. Although some cockatiels do learn to repeat phrases, males are generally better at mimicry than females. Cockatiel speech often comes out as a "whistle" when they do annunciate, the voice being soft in volume and difficult to make out. Cockatiels can mimic many sounds, such as the bleep of a car alarm, a ringing telephone, the sound of a zipper, the beeping of cell phones or microwaves, or the calls of other bird species such as blue jays or chickadees and loud weather like thunder. They can also mimic other pets such as dogs, occasionally barking back.
Although some say that female cockatiels cannot speak, this is not an absolute. Males have been known to mimic noises, words and sometimes other animals. Females generally don't imitate speech, but tend to mimic sounds such as telephones, washing machines, toilet flushes, etc. Cockatiels that do imitate speech will usually mimic frequently heard phrases, particularly of the individual to whom the bird feels closest.
Breeding
Cockatiels are a popular choice for amateur parrot breeders along with budgerigars. This is due to both the ease of getting the birds to breed (they seem to have no inhibitions, with both genders engaging in self-stimulation) and the fairly low cost of the equipment needed. Generally a clutch consists of 4-5 eggs, each approximately the size of one's thumbnail. Eggs are laid once every two days and incubate for about 19 days. Hatchlings are weaned in 4 weeks, and can fly around 2 months. Puberty (adolescence) is reached around 9 months of age while adulthood is reached around 1 year and 9 months in males and/or 15 months in females.
Male cockatiels are very protective and nurturing of their offspring and are known to be very capable of raising their newborns if the mother is unable to.
Some female cockatiels also lay eggs without fertilization, much as those of the chicken species used for food production. In this event, the owner should leave the eggs alone until the bird stops sitting on them, after which the eggs can be removed. To prevent laying, one can keep the cockatiel in more darkness per day by covering it earlier in the evening and leaving the cage covered longer in the morning. Like all parrots, cockatiels of either gender can grow to see their owner or a toy as a mate, engage in courtship and mating behaviour including territoriality, and females may lay infertile eggs.
It has been suggested by some breeders that petting the back of the female cockatiel may inadvertently sexually stimulate the hen, promoting egg-laying, and that owners seeking to avoid egg-laying should avoid this particular form of bonding.
The Cockatiel has recently been shown to be capable of hybridising with the Galah, producing offspring described by the media as 'Galatiels'.
Colour mutations
About fifteen primary mutations have been established in the species and enable the production of many different combinations.
Note : aka stands for also-known-as, cka stands for commonly-known-as & ika stands for incorrectly-known-as
- ADMpied (aka Recessive Pied aka Harlequin)
- Ashenfallow (ika Recessive silver)
- Bronzefallow (cka Brownfallow)
- Cinnamon
- Dilute (ika Pastel Silver)
- Dominant silver (aka Ashen Dilute)
- Edged dilute (ika Spangled ika spangled silver)
- Faded
- SL Ino
- NSLino (Recessive Ino)
- Opaline (cka Pearled)
- Palefaced (ika Pastelface)
- Platinum (ika Pallid)
- Whitefaced (same gene as genuine Blue mutation in typical Parrot & Parakeet species)
- Dominant and Sex Linked Yellowcheeked
- Yellow-suffused (ika Emerald, or Olive)
The multiple names for these mutations is due in part to different regions of the globe naming the same colour change a different term. This does not mean that it is a different mutation. It only means it is a different name.
Colour mutations are a natural phenomenon equally occurring in captivity and in the wild.
The "Normal Grey" or "Wild-type" cockatiel's plumage is primarily grey with prominent white flashes on the outer edges of each wing. The face of the male is yellow or white, while the face of the female is primarily grey or light grey, and both genders feature a round orange area on both ear areas, often referred to as "cheek patches." This orange colouration is generally vibrant in adult males, and often quite muted in females. Visual sexing is often possible with this variant of the bird.
"Whiteface" cockatiels have their yellow pigments deactivated by an autosomal recessive gene, resulting in a cock with a truly white face and a hen with a more typical mottled grey face. This means, there is no yellow or orange colouring in a whiteface cockatiel.
The "Lutino" sex-linked recessive mutation is a perfect example of a type of cockatiel that are the hardest to sex visually. Lutinos lack eumelanin pigment (enabling black, brown, grey colours and tones) and are consequently yellow to yellowish-white with orange cheek-patches. Adult female Lutinos as well as immature Lutinos of both genders display yellow bars, dots and/or stripes on the underside of their tail feathers. While mature males always display solid white coloured undersides of tail-feathers.
Unfortunately, a good number of Cockatiels of all Ino mutations & varieties (Albino ika Whitefaced Ino, Palefaced Ino aka Creamino, Lutino, Opaline-Ino aka Pearlino...etc) are usually affected with a transmittable genetic flaw monstrously enlarging the bald-spot below the crest, due to intense overbreeding and a general lack of breeders to breed it out.
"Pied" cockatiel plumage patterns vary significantly from animal to animal, giving rise to cockatiel breeders & hobbyists' "heavy pied" and "light pied" loose distinctions. Unfortunately, the degree in piedness remains virtually unpredictable genetically. However, breeding heavily pied specimens together generally produces a higher percentage of heavily pied offsprings than breeding lesser pied specimens together. Ultimately, the "pied" mutation causes the bird to lack a majority of the typical gray plumage on the breast, belly, and head. Thus "pied" cockatiels are characterised by the degree of their yellow or yellow-white colouring in these areas.
It is important to know that, throughout Parrot species the ADMpied (AntiDiMorphic Pied) gene negates the male's ability from ever displaying his species' sexual-dimorphic features. Leading to ADMpied cockatiels being notoriously difficult to sex visually but being excellent examples for studies in genetic traits. However, in Mono-Morphic species (i.e. Conures, Lovebirds, Macaws, Rosellas...) the Anti-Di-Morphic (hence ADMpied) feature cannot be expressed but Piedness still is and in these species such Pied specimens are called either Recessivepied &/or Harlequin.
Cinnamon and Opaline ("Pearled") mutations are sex-linked recessive. In Cinnamons, the melanin pigment is modified in such a way that eumelanin pigments are stopped at the brown stage of their development to becoming black. Here is an excellent description of the pearled cockatiel:
The Pearl Cockatiels gene does not have any visual affect on the colour pigments in the bird but instead it affects the distribution of the colours that are already present. It actually decreases the spread of the grey family of pigments (melanin) and increases the spread of the yellow pigments (psittacins). Individual feathers over most of a pearled bird will have more of the yellow family of pigments visible giving them a scalloped pattern.
It is especially interesting to note that males do not retain the pearled colourings. They soon lose this after their first molt. Though you may not be able to see this pattern, it is not essentially gone. It is only covered up by more grey pigment.
There are a tremendous number of colour varieties (combined mutations), including ADMpied Cinnamon, Albino (ika Whitefaced Ino), Opaline Cinnamon (aka Pearled Cinnamon), Palefaced Lutino (aka Creamino), Whitefaced Cinnamon, Whitefaced Opaline (Pearl) and so on ...
The Albino (ika Whitefaced Ino) Cockatiel is the exact genetic equivalent of any other Albino combination mutation in other Parrot species such as the Budgerigar, the celestial aka Pacific Parrotlet, the Indian-ringnecked aka Rose-ringed Parakeet, the splendid aka Scarlet-chested Parrot and the white-eye-ringed Lovebird species. This mutation is always produced by combining the genuine Whitefaced mutation (otherwise called Blue mutation in all Lories, Lorikeets &/or typical Parrot species) and Complete Albinistic (either NSLino &/or SL Ino) mutations together.
Mutations can appear both individually or in a wide variety of combinations such as Albino (ika Whitefaced Ino), Pearled Lutino (aka PearlIno), Whitefaced Pied, Opaline-Cinnamon (aka Pearled-Cinnamon)... Still fairly hard to find is the rather new Yellow-suffused (ika 'Emerald &/or 'Olive') mutation. Cockatiels do not actually have green pigment to their plumage, thus Yellow-suffused specimens don't either. The yellow suffusion combined with underlying black (or brown in Cinnamon specimens) pigmentation produces an illusion of greenish tones giving rise to the genetically incorrect common names of 'Emerald &/or 'Olive' for this trait.
Many mutations retain the normal features (black eyes, grey beak, grey feet/skin & black toe nails) of Wild-type (Grey) Cockatiel Parakeets. However, ;
Fallow & Ino mutations have pink to red eyes, pink feet, clear (pink) toe nails & pinkish-white beaks.
Cinnamon specimens look quite alike the Wildtype (aka Normal Grey) specimens, with the exception of being pure-brown where Wildtypes are grey.
Sex-linked mutations such as Cinnamon, Ino, Opaline, Platinum (ika 'Pallid') &/or SL-Yellowfaced have a higher ratio of female offspring to male due to the mode of inheritance from parents to offspring.




